Achieving behavioral control with millisecond resolution in a high-level programming environment
- PMID: 18606188
- PMCID: PMC2581819
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.06.003
Achieving behavioral control with millisecond resolution in a high-level programming environment
Abstract
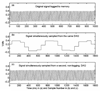
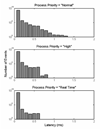
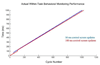
The creation of psychophysical tasks for the behavioral neurosciences has generally relied upon low-level software running on a limited range of hardware. Despite the availability of software that allows the coding of behavioral tasks in high-level programming environments, many researchers are still reluctant to trust the temporal accuracy and resolution of programs running in such environments, especially when they run atop non-real-time operating systems. Thus, the creation of behavioral paradigms has been slowed by the intricacy of the coding required and their dissemination across labs has been hampered by the various types of hardware needed. However, we demonstrate here that, when proper measures are taken to handle the various sources of temporal error, accuracy can be achieved at the 1 ms time-scale that is relevant for the alignment of behavioral and neural events.
Figures



References
-
- Ghose GM, Ohzawa I, Freeman RD. A flexible PC-based physiological monitor for animal experiments. J Neurosci Methods. 1995;62:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Hays AV, Richmond BJ, Optican LM. A UNIX-based multiple-process system for real-time data acquisition and control; WESCON Conference Proceedings; 1982. pp. 1–10.
-
- Maunsell JHR. LabLib. 2008. http://maunsell.med.harvard.edu/software.html.
-
- Meyer T, Constantinidis C. A software solution for the control of visual behavioral experimentation. J Neurosci Methods. 2005;142:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Ramamritham K, Shen C, Sen S, Shirgurkar S. Using Windows NT for Real-Time Applications: Experimental Observations and Recommendations; IEEE Real Time Technology and Applications Symposium; 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

