Iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis and human disease
- PMID: 18606475
- PMCID: PMC2574672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.05.008
Iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis and human disease
Abstract
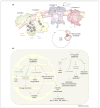
Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters are essential for numerous biological processes, including mitochondrial respiratory chain activity and various other enzymatic and regulatory functions. Human Fe-S cluster assembly proteins are frequently encoded by single genes, and inherited defects in some of these genes cause disease. Recently, the spectrum of diseases attributable to abnormal Fe-S cluster biogenesis has extended beyond Friedreich ataxia to include a sideroblastic anemia with deficiency of glutaredoxin 5 and a myopathy associated with a deficiency of a Fe-S cluster assembly scaffold protein, ISCU. Mutations within other mammalian Fe-S cluster assembly genes could be causative for human diseases that manifest distinctive combinations of tissue-specific impairments. Thus, defects in the iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis pathway could underlie many human diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Johnson DC, et al. Structure, function, and formation of biological iron-sulfur clusters. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:247–281. - PubMed
-
- Lill R, Muhlenhoff U. Maturation of iron-sulfur proteins in eukaryotes: mechanisms, connected processes, and diseases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008;77:669–700. - PubMed
-
- Rudolf J, et al. The DNA repair helicases XPD and FancJ have essential iron-sulfur domains. Mol Cell. 2006;23:801–808. - PubMed
-
- Rouault TA. The role of iron regulatory proteins in mammalian iron homeostasis and disease. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:406–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

