Inhibition of neutral endopeptidase potentiates neutrophil activation during Mg-deficiency in the rat
- PMID: 18607539
- PMCID: PMC3715053
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-007-7186-z
Inhibition of neutral endopeptidase potentiates neutrophil activation during Mg-deficiency in the rat
Abstract
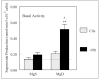
Neutral endopeptidase (NEP), which degrades substance P (SP), may regulate neutrophil activation during Mg-deficiency (MgD). Male Sprague-Dawley rats (180g) were fed MgD (approximately 50 mg Mg/kg) or Mg-sufficient (MgS, 608 mg Mg/kg) diets for 7 days +/- NEP inhibitor phosphoramidon (PR, 5 mg/kg/day, s.c.). MgD alone induced a 9-fold (vs. MgS, p <0.01) elevation in plasma SP; MgD+PR enhanced it further to 18-fold (p <0.001). Neutrophils from MgD+PR rats displayed a 3.9-fold higher (p <0.01) basal .O(2-) generation, but those from MgD or PR alone were not activated. Plasma PGE2-metabolite levels rose 2.67- (p <0.01) and 1.56- (p <0.05) fold, respectively, in MgD+PR and MgD groups; the corresponding red blood cell glutathione levels were decreased 21% (p <0.025) and 7% (NS). MgD+PR significantly reduced neutrophil NEP activity by 48% (p <0.02); PR or MgD alone only reduced this activity 26% and 15%, respectively. We conclude that NEP inhibition potentiates SP-mediated neutrophil .O(2-) production and may promote other inflammatory activities during MgD.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Neutral endopeptidase inhibition enhances substance P mediated inflammation due to hypomagnesemia.Magnes Res. 2009 Sep;22(3):167S-173S. Magnes Res. 2009. PMID: 19780404 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of neutrophil and endothelial activation by substance P receptor blockade in the Mg-deficient rat.Magnes Res. 2003 Jun;16(2):91-7. Magnes Res. 2003. PMID: 12892378
-
Neutral endopeptidase modulates substance P-induced activation of human neutrophils.Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;93(2-3):133-8. doi: 10.1159/000235292. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990. PMID: 1712001
-
Loss of neutral endopeptidase activity contributes to neutrophil activation and cardiac dysfunction during chronic hypomagnesemia: Protection by substance P receptor blockade.Exp Clin Cardiol. 2011 Winter;16(4):121-4. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 22131854 Free PMC article.
-
Magnesium-deficiency-enhanced post-ischemic myocardial injury is reduced by substance P receptor blockade.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1997 Jan;29(1):97-110. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1996.0255. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1997. PMID: 9040025
Cited by
-
Neutral endopeptidase inhibition enhances substance P mediated inflammation due to hypomagnesemia.Magnes Res. 2009 Sep;22(3):167S-173S. Magnes Res. 2009. PMID: 19780404 Free PMC article.
-
d-Propranolol protects against oxidative stress and progressive cardiac dysfunction in iron overloaded rats.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Sep;90(9):1257-68. doi: 10.1139/y2012-091. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22913465 Free PMC article.
-
The Bidirectional Effects of Periodontal Disease and Oral Dysbiosis on Gut Inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.J Crohns Colitis. 2025 Apr 4;19(4):jjae162. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae162. J Crohns Colitis. 2025. PMID: 39447062
-
The role of magnesium deficiency in cardiovascular and intestinal inflammation.Magnes Res. 2010 Dec;23(4):S199-206. doi: 10.1684/mrh.2010.0218. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Magnes Res. 2010. PMID: 20971697 Free PMC article.
-
AZT-induced oxidative cardiovascular toxicity: attenuation by Mg-supplementation.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2009 Jun;9(2):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s12012-009-9040-8. Epub 2009 May 12. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19484392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weglicki WB, Mak IT, Phillips TM. Blockade of cardiac inflammation in Mg2+-deficiency by substance P receptor inhibition. Circ Res. 1994;24:1009–13. - PubMed
-
- Weglicki WB, Mak IT, Stafford RE, Dickens BF, Cassidy MM, Phillips TM. Neurogenic peptides and the cardiomyopathy of magnesium deficiency: Effects of substance P-receptor inhibition. Mol Cell Biochem. 1994;130:103–9. - PubMed
-
- Kramer JH, Mak IT, Phillips TM, Weglicki WB. Dietary magnesium intake influence circulating pro-inflammatory neuropeptide levels and loss of myocardial tolerance to postischemic stress. Exp Biol Med. 2003;228:665–73. - PubMed
-
- Tejero-Taldo MI, Chmielinska JJ, Gonzalez G, Mak IT, Weglicki WB. N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor blockade inhibits cardiac inflammation in the Mg-deficient rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;311:8–13. - PubMed
-
- Mak IT, Dickens BF, Komarov AM, Phillips TM, Weglicki WB. Activation of the neutrophil and loss of plasma glutathione during Mg-deficiency – modulation effect by nitric oxide synthase inhibition. Mol Cell Biochem. 1997;176:35–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

