Inhibition of protein synthesis by imexon reduces HIF-1alpha expression in normoxic and hypoxic pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 18607542
- PMCID: PMC2607477
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-008-9149-9
Inhibition of protein synthesis by imexon reduces HIF-1alpha expression in normoxic and hypoxic pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
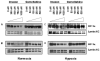
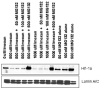
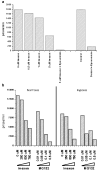
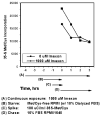
Hypoxia-inducing factor-1 alpha (HIF-1alpha), is a major survival factor for tumor cells growing in a low oxygen environment. The anti-cancer agent imexon binds thiols and causes accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in pancreatic cancer cells. Unlike many cytotoxic agents, imexon is equi-cytotoxic in human MiaPaCa-2 and Panc-1 cells grown in normoxic (21% O(2)) and hypoxic (1% O(2)) conditions. Western blot analyses of imexon-treated cells demonstrated that imexon reduces HIF-1alpha protein levels in both normoxic and hypoxic conditions in a time- and concentration-dependant fashion. Gemcitabine did not similarly affect HIF-1alpha levels. Imexon did not reduce transcription of new HIF-1alpha mRNA, but did reduce the synthesis of new proteins, including HIF-1alpha, measured by (35)S methionine/cysteine (Met/Cys) incorporation. Concurrently, the half-life of existing HIF-1alpha protein was increased by imexon, in association with a marked inhibition of chymotryptic activity in the 20S proteasome. The inhibition of HIF-1alpha translation was not specific, rather it was part of a general decrease in protein translation caused by imexon. This inhibitory effect on translation did not involve phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor-2alpha (eIF-2alpha) and was not closely correlated to cell growth inhibition by imexon, suggesting that mechanisms other than protein synthesis inhibition contribute to the drug's cytotoxic effects. In summary, imexon blocks the translation of new proteins, including HIF-1alpha, and this effect overcomes an increase in the stability of preformed HIF-1alpha due to proteasome inhibition by imexon. Because net HIF-1alpha levels are reduced by imexon, combination studies with other drugs affected by HIF-1alpha survival signaling are warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lenticular cytoprotection. Part 1: the role of hypoxia inducible factors-1α and -2α and vascular endothelial growth factor in lens epithelial cell survival in hypoxia.Mol Vis. 2013;19:1-15. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23335846 Free PMC article.
-
An undesired effect of chemotherapy: gemcitabine promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness through reactive oxygen species-dependent, nuclear factor κB- and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α-mediated up-regulation of CXCR4.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 19;288(29):21197-21207. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.484576. Epub 2013 Jun 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23740244 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression and gemcitabine chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer.Oncol Rep. 2011 Dec;26(6):1399-406. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1457. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Oncol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21922147
-
Hypoxia regulates ABCG2 activity through the activivation of ERK1/2/HIF-1α and contributes to chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2016;17(2):188-98. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1139228. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26785721 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein in hypoxia occurs independently of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 8;285(41):31277-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.158485. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20675386 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Insig2 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and its expression is induced by hypoxia.Cancer Sci. 2011 Jun;102(6):1137-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01936.x. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21443541 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and significance of MMP2 and HIF-1α in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2014 Aug;8(2):539-546. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2189. Epub 2014 May 28. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25013467 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-tumor activity and mechanism of action for a cyanoaziridine-derivative, AMP423.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;69(4):1039-49. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1784-8. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22186884 Free PMC article.
-
Bufalin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis by targeting HIF-1α via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 12;7(15):20193-208. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7935. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26958938 Free PMC article.
-
A phase I study of imexon plus gemcitabine as first-line therapy for advanced pancreatic cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;66(2):287-94. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-1162-y. Epub 2009 Oct 24. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19855966 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Dragovich T, Gordon M, Mendeslon D, et al. Phase I trial of imexon in patients with advanced malignancy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1779–1784. - PubMed
-
- Cohen SJ, Zalupski M, Modiano M, Conkling P, Patt Y, Davis P, Dorr R, Boytim M, Hersh E. A phase I study of Amplimexon (AMP, imexon inj.) plus gemcitabine (Gem) as first line therapy in advanced pancreatic cancer (PC) with preclinical mechanistic study of dose limiting toxicity (DLT). Proceedings of the ASCO Annual Meeting.2008.
-
- Iyengar BS, Dorr RT, Remers WA. Chemical basis for the biological activity of imexon and related cyanoaziridines. J Med Chem. 2004;47:218–223. - PubMed
-
- Dvorakova K, Payne CM, Tome ME, Briehl MM, McClure T, Dorr RT. Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis in myeloma cells by the aziridine-containing agent imexon. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000;60:749–758. - PubMed
-
- Dvorakova K, Waltmire CN, Payne CM, Tome ME, Briehl MM, Dorr RT. Induction of mitochondrial changes in myeloma cells by imexon. Blood. 2001;97:3544–3551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

