Specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors regulate human osteosarcoma cells in vitro
- PMID: 18607665
- PMCID: PMC2493014
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0338-9
Specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors regulate human osteosarcoma cells in vitro
Abstract
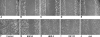
Inhibitors of specific tyrosine kinases are attractive lead compounds for development of targeted chemotherapies for many tumors, including osteosarcoma. We asked whether inhibition of specific tyrosine kinases would decrease the motility, colony formation, and/or invasiveness by human osteosarcoma cell lines (TE85, MNNG, 143B, SAOS-2, LM-7). An EGF-R inhibitor reduced motility of all five cell lines by 50% to 80%. In contrast, an IGF-1R inhibitor preferentially reduced motility by 42% in LM-7 cells and a met inhibitor preferentially reduced motility by 80% in MNNG cells. The inhibitors of EGF-R, IGF-1R, and met reduced colony formation by more than 80% in all tested cell lines (TE85, MNNG, 143B). The EGF-R inhibitor reduced invasiveness by 62% in 143B cells. The JAK inhibitor increased motility of SAOS-2 and LM7 cells without affecting colony formation or invasiveness. Inhibitors of HER-2, NGF-R, and PDGF-Rs did not affect motility, invasiveness, or colony formation. These results support the hypothesis that specific tyrosine kinases regulate tumorigenesis and/or metastasis in osteosarcoma.
Figures
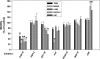



References
-
- Albini A, Iwamoto Y, Kleinman HK, Martin GR, Aaronson SA, Kozlowski JM, McEwan RN. A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1987;47:3239–3245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

