Occupational transmission of Acinetobacter baumannii from a United States serviceman wounded in Iraq to a health care worker
- PMID: 18611162
- PMCID: PMC4074882
- DOI: 10.1086/589247
Occupational transmission of Acinetobacter baumannii from a United States serviceman wounded in Iraq to a health care worker
Abstract
Background: Acinetobacter baumannii is increasingly recognized as being a significant pathogen associated with nosocomial outbreaks in both civilian and military treatment facilities. Current analyses of these outbreaks frequently describe patient-to-patient transmission. To date, occupational transmission of A. baumannii from a patient to a health care worker (HCW) has not been reported. We initiated an investigation of an HCW with a complicated case of A. baumannii pneumonia to determine whether a link existed between her illness and A. baumannii-infected patients in a military treatment facility who had been entrusted to her care.
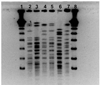
Methods: Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and polymerase chain reaction/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, a form of multilocus sequencing typing, were done to determine clonality. To further characterize the isolates, we performed a genetic analysis of resistance determinants.
Results and conclusions: A "look-back" analysis revealed that the multidrug resistant A. baumannii recovered from the HCW and from a patient in her care were indistinguishable by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. In addition, polymerase chain reaction/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry indicated that the isolates were similar to strains of A. baumannii derived from European clone type II (Walter Reed Army Medical Center strain type 11). The exposure of the HCW to the index patient lasted for only 30 min and involved endotracheal suctioning without use of an HCW mask. An examination of 90 A. baumannii isolates collected during this investigation showed that 2 major and multiple minor clone types were present and that the isolates from the HCW and from the index patient were the most prevalent clone type. Occupational transmission likely occurred in the hospital; HCWs caring for patients infected with A. baumannii should be aware of this potential mode of infection spread.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Zeana C, Larson E, Sahni J, Bayuga SJ, Wu F, Della-Latta P. The epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: does the community represent a reservoir? Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2003;24:275–279. - PubMed
-
- Fournier PE, Richet H. The epidemiology and control of Acinetobacter baumannii in health care facilities. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:692–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

