Histone deacetylase inhibitors up-regulate astrocyte GDNF and BDNF gene transcription and protect dopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 18611290
- PMCID: PMC2579941
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145708009024
Histone deacetylase inhibitors up-regulate astrocyte GDNF and BDNF gene transcription and protect dopaminergic neurons
Abstract
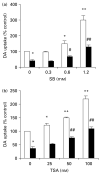
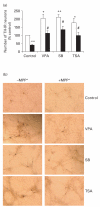
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by the selective and progressive loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the midbrain substantia nigra. Currently, available treatment is unable to alter PD progression. Previously, we demonstrated that valproic acid (VPA), a mood stabilizer, anticonvulsant and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, increases the expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in astrocytes to protect DA neurons in midbrain neuron-glia cultures. The present study investigated whether these effects are due to HDAC inhibition and histone acetylation. Here, we show that two additional HDAC inhibitors, sodium butyrate (SB) and trichostatin A (TSA), mimic the survival-promoting and protective effects of VPA on DA neurons in neuron-glia cultures. Similar to VPA, both SB and TSA increased GDNF and BDNF transcripts in astrocytes in a time-dependent manner. Furthermore, marked increases in GDNF promoter activity and promoter-associated histone H3 acetylation were noted in astrocytes treated with all three compounds, where the time-course for acetylation was similar to that for gene transcription. Taken together, our results indicate that HDAC inhibitors up-regulate GDNF and BDNF expression in astrocytes and protect DA neurons, at least in part, through HDAC inhibition. This study indicates that astrocytes may be a critical neuroprotective mechanism of HDAC inhibitors, revealing a novel target for the treatment of psychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Armstrong KJ, Niles LP. Induction of GDNF mRNA expression by melatonin in rat C6 glioma cells. Neuroreport. 2002;13:473–475. - PubMed
-
- Beck KD, Valverde J, Alexi T, Poulsen K, Moffat B, Vandlen RA, Rosenthal A, Hefti F. Mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons protected by GDNF from axotomy-induced degeneration in the adult brain. Nature. 1995;373:339–341. - PubMed
-
- Burke RE, Antonelli M, Sulzer D. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic growth factor inhibits apoptotic death of postnatal substantia nigra dopamine neurons in primary culture. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1998;71:517–525. - PubMed
-
- Canudas AM, Pezzi S, Canals JM, Pallas M, Alberch J. Endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects dopaminergic nigral neurons against transneuronal degeneration induced by striatal excitotoxic injury. Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research. 2005;134:147–154. - PubMed
-
- Castro LM, Gallant M, Niles LP. Novel targets for valproic acid: up-regulation of melatonin receptors and neurotrophic factors in C6 glioma cells. Journal of Neurochemistry. 2005;95:1227–1236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

