Novel genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato from rodents and ticks in southwestern China
- PMID: 18614645
- PMCID: PMC2546722
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01195-08
Novel genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato from rodents and ticks in southwestern China
Abstract
By using multilocus sequence analysis, five Borrelia valaisiana-related strains isolated from rodents and ticks in southwestern China were eventually classified as a new genospecies of B. burgdorferi sensu lato rather than B. valaisiana. The finding explained the differences in transmission cycle and phenotype between B. valaisiana strains from Europe and B. valaisiana-related strains from eastern Asia.
Figures
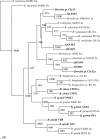

References
-
- Kee, S. H., J. H. Yoon, H. B. Oh, Y. H. Park, Y. W. Kim, M. K. Cho, K. S. Park, and W. H. Chang. 1996. Genetic analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Korea using genomic hybridization and 16S rRNA gene sequence determination. Microbiol. Immunol. 40599-605. - PubMed
-
- Masuzawa, T., T. Fukui, M. Miyake, H. B. Oh, M. K. Cho, W. H. Chang, Y. Imai, and Y. Yanagihara. 1999. Determination of members of a Borrelia afzelii-related group isolated from Ixodes nipponensis in Korea as Borrelia valaisiana. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 491409-1415. - PubMed
-
- Masuzawa, T., N. Hashimoto, M. Kudeken, T. Kadosaka, M. Nakamura, H. Kawabata, N. Koizumi, and Y. Imai. 2004. New genomospecies related to Borrelia valaisiana, isolated from mammals in Okinawa archipelago, Japan. J. Med. Microbiol. 53421-426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

