Changing patterns in frequency of recovery of five methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones in Portuguese hospitals: surveillance over a 16-year period
- PMID: 18614664
- PMCID: PMC2546730
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00692-08
Changing patterns in frequency of recovery of five methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones in Portuguese hospitals: surveillance over a 16-year period
Abstract
A total of 629 nonduplicate methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus MRSA isolates were recovered between June and November 2006 from 11 hospitals located in different areas of Portugal. Selected isolates (n = 271, 43%) were typed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), representatives of which were additionally characterized by spa typing, multilocus sequence typing, staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) typing, and the presence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL). The 271 isolates were classified into 13 different clonal types. Three pandemic clones included the majority (n = 241, 88%) of the isolates and were observed in several hospitals: (i) EMRSA-15 (54%)-PFGE type A, ST22, spa type t022, SCCmec IV-was found in the 11 hospitals studied and was identified as the major clone in seven of them; (ii) the New York/Japan clone (17%)-PFGE B, ST5, spa type t067, SCCmec II-was identified in nine hospitals and represented the major clone in four; and (iii) the Brazilian MRSA (17%)-PFGE C, ST239, spa type t037, SCCmec IIIA-was also detected in nine hospitals but never as the main clone. All isolates tested were PVL negative. Clone EMRSA-15 is currently the predominant MRSA clonal type circulating in Portuguese hospitals, but a new wave of MRSA has emerged in the country with the recent introduction and spread of the New York/Japan clone. The Brazilian MRSA that was the leading clone in Portugal in the late 1990s is declining and being progressively replaced by the two former clones. We report the first isolate SCCmec type V (ST45) in Portugal.
Figures

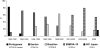
References
-
- Aires de Sousa, M., and H. de Lencastre. 2004. Bridges from hospitals to the laboratory: genetic portraits of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 40101-111. - PubMed
-
- Aires de Sousa, M., H. de Lencastre, I. Santos Sanches, K. Kikuchi, K. Totsuka, and A. Tomasz. 2000. Similarity of antibiotic resistance patterns and molecular typing properties of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates widely spread in hospitals in New York City and in a hospital in Tokyo, Japan. Microb. Drug Resist. 6253-258. - PubMed
-
- Aires de Sousa, M., M. Miragaia, I. S. Sanches, S. Avila, I. Adamson, S. T. Casagrande, M. C. Brandileone, R. Palacio, L. Dell'Acqua, M. Hortal, T. Camou, A. Rossi, M. E. Velazquez-Meza, G. Echaniz-Aviles, F. Solorzano-Santos, I. Heitmann, and H. de Lencastre. 2001. Three-year assessment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones in Latin America from 1996 to 1998. J. Clin. Microbiol. 392197-2205. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

