Atrial natriuretic peptide frameshift mutation in familial atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 18614783
- PMCID: PMC2518320
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0706300
Atrial natriuretic peptide frameshift mutation in familial atrial fibrillation
Abstract
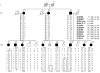
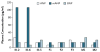
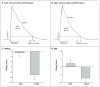
Atrial fibrillation is a common arrhythmia that is hereditary in a small subgroup of patients. In a family with 11 clinically affected members, we mapped an atrial fibrillation locus to chromosome 1p36-p35 and identified a heterozygous frameshift mutation in the gene encoding atrial natriuretic peptide. Circulating chimeric atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) was detected in high concentration in subjects with the mutation, and shortened atrial action potentials were seen in an isolated heart model, creating a possible substrate for atrial fibrillation. This report implicates perturbation of the atrial natriuretic peptide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) pathway in cardiac electrical instability.
2008 Massachusetts Medical Society
Figures
References
-
- Braunwald E. Cardiovascular medicine at the turn of the millennium: triumphs, concerns, and opportunities. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1360–9. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2004;110:1042–6. - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Parise H, D’Agostino RB, et al. Parental atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation in offspring. JAMA. 2004;291:2851–5. - PubMed
-
- Gudbjartsson DF, Arnar DO, Helgadottir A, et al. Variants conferring risk of atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Nature. 2007;448:353–7. - PubMed
-
- Brugada R, Tapscott T, Czernuszewicz GZ, et al. Identification of a genetic locus for familial atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:905–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
