HIV-1 persists in breast milk cells despite antiretroviral treatment to prevent mother-to-child transmission
- PMID: 18614871
- PMCID: PMC2765916
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328302cc11
HIV-1 persists in breast milk cells despite antiretroviral treatment to prevent mother-to-child transmission
Abstract
Background: The effects of short-course antiretrovirals given to reduce mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) on temporal patterns of cell-associated HIV-1 RNA and DNA in breast milk are not well defined.
Methods: Women in Kenya received short-course zidovudine (ZDV), single-dose nevirapine (sdNVP), combination ZDV/sdNVP or short-course highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Breast milk samples were collected two to three times weekly for 4-6 weeks. HIV-1 DNA was quantified by real-time PCR. Cell-free and cell-associated RNA levels were quantified by the Gen-Probe HIV-1 viral load assay.
Results: Cell-free HIV-1 RNA levels in breast milk were significantly suppressed by sdNVP, ZDV/sdNVP or HAART therapy compared with ZDV between day 3 and week 4 postpartum (P < or = 0.03). Breast milk HIV-1 DNA levels (infected cell levels) were not significantly different between treatment arms at any timepoint during the 4-6-week follow-up. At 3 weeks postpartum, when the difference in cell-free RNA levels was the greatest comparing HAART directly with ZDV (P = 0.0001), median log10 HIV-1 DNA copies per 1 x 10 cells were 2.78, 2.54, 2.69, and 2.31 in the ZDV, sdNVP, ZDV/sdNVP and HAART arms, respectively (P = 0.23). Cell-associated HIV-1 RNA levels were modestly suppressed in HAART versus ZDV/sdNVP during week 3 (3.37 versus 4.02, P = 0.04), as well as over time according to a linear mixed-effects model.
Conclusion: Cell-free and, to a lesser extent, cell-associated HIV-1 RNA levels in breast milk were suppressed by antiretroviral regimens used to prevent MTCT. However, even with HAART, there was no significant reduction in the reservoir of infected cells, which could contribute to breast milk HIV-1 transmission.
Figures

 (× symbol), sdNVP
(× symbol), sdNVP  (square symbol), ZDV/sdNVP —— (circle symbol), and HAART
(square symbol), ZDV/sdNVP —— (circle symbol), and HAART  (triangle symbol).
(triangle symbol).
 (× symbol), sdNVP
(× symbol), sdNVP  (square symbol), ZDV/sdNVP —— (circle symbol), HAART
(square symbol), ZDV/sdNVP —— (circle symbol), HAART  (triangle symbol). BMC, breast milk cell.
(triangle symbol). BMC, breast milk cell.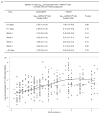
 , long-dash dotted line). BMC, breast milk cell.
, long-dash dotted line). BMC, breast milk cell.
References
-
- Nduati R, John G, Mbori-Ngacha D, Richardson B, Overbaugh J, Mwatha A, et al. Effect of breastfeeding and formula feeding on transmission of HIV-1: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2000;283:1167–1174. - PubMed
-
- Coutsoudis A, Dabis F, Fawzi W, Gaillard P, Haverkamp G, Harris DR, et al. Late postnatal transmission of HIV-1 in breast-fed children: an individual patient data meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:2154–2166. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Antiretroviral drugs for treating pregnant women and preventing HIV infection in infant: towards universal access. Recommendations for a public health approach. 2006. [Accessed October 2007]. http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/pmtctguidelines3.pdf. - PubMed
-
- Shaffer N, Chuachoowong R, Mock PA, Bhadrakom C, Siriwasin W, Young NL, et al. Short-course zidovudine for perinatal HIV-1 transmission in Bangkok, Thailand: a randomised controlled trial. Bangkok Collaborative Perinatal HIV Transmission Study Group. Lancet. 1999;353:773–780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

