Neuronal cell death in Alzheimer's disease and a neuroprotective factor, humanin
- PMID: 18615127
- PMCID: PMC2430668
- DOI: 10.2174/157015906776359577
Neuronal cell death in Alzheimer's disease and a neuroprotective factor, humanin
Abstract
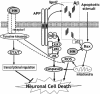
Brain atrophy caused by neuronal loss is a prominent pathological feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Amyloid beta (Abeta), the major component of senile plaques, is considered to play a central role in neuronal cell death. In addition to removal of the toxic Abeta, direct suppression of neuronal loss is an essential part of AD treatment; however, no such neuroprotective therapies have been developed. Excess amount of Abeta evokes multiple cytotoxic mechanisms, involving increase of the intracellular Ca(2+) level, oxidative stress, and receptor-mediated activation of cell-death cascades. Such diversity in cytotoxic mechanisms induced by Abeta clearly indicates a complex nature of the AD-related neuronal cell death. We have identified a 24-residue peptide, Humanin (HN), which suppresses in vitro neuronal cell death caused by all AD-related insults, including Abeta, so far tested. The anti-AD effect of HN has been further confirmed in vivo using mice with Abeta-induced amnesia. Altogether, such potent neuroprotective activity of HN against AD-relevant cytotoxicity both in vitro and in vivo suggests the potential clinical applications of HN in novel AD therapies aimed at controlling neuronal death.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Humanin (HN); amyloid precursor protein (APP); amyloid β; neuronal death; neuroprotection; presenilin (PS).
Figures


References
-
- Abe Y, Hashimoto Y, Tomita Y, Terashita K, Aiso S, Tajima H, Niikura T, Matsuoka M, Nishimoto I. Cytotoxic mechanisms by M239V presenilin 2, a little-analyzed Alzheimer’s disease-causative mutant. J Neurosci Res. 2004;77:583–595. - PubMed
-
- Abe Y, Kouyama K, Tomita T, Tomita Y, Ban N, Nawa M, Matsuoka M, Niikura T, Aiso S, Kita Y, Iwatsubo T, Nishimoto I. Analysis of neurons created from wild-type and Alzheimer’s mutation knock-in embryonic stem cells by a highly efficient differentiation protocol. J Neurosci. 2003;23:8513–8525. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araki W, Yuasa K, Takeda S, Shirotani K, Takahashi K, Tabira T. Overexpression of presenilin-2 enhances apoptotic death of cultured cortical neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;920:241–244. - PubMed
-
- Benaki D, Zikos C, Evangelou A, Livaniou E, Vlassi M, Mikros E, Pelecanou M. Solution structure of Humanin, a peptide against Alzheimer’s disease-related neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;329:152–160. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Thinakaran G, Eckman CB, Lee MK, Davenport F, Ratovitsky T, Prada CM, Kim G, Seekins S, Yager D, Slunt HH, Wang R, Seeger M, Levey AI, Gandy SE, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL, Younkin SG, Sisodia SS. Familial Alzheimer’s disease-linked presenilin 1 variants elevate Aβ1-42/1-40 ratio in vitro and in vivo. Neuron. 1996;17:1005–1013. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
