Serotonin as a modulator of glutamate- and GABA-mediated neurotransmission: implications in physiological functions and in pathology
- PMID: 18615128
- PMCID: PMC2430669
- DOI: 10.2174/157015906776359540
Serotonin as a modulator of glutamate- and GABA-mediated neurotransmission: implications in physiological functions and in pathology
Abstract
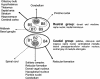
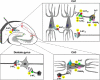
The neurotransmitter serotonin (5-HT), widely distributed in the central nervous system (CNS), is involved in a large variety of physiological functions. In several brain regions 5-HT is diffusely released by volume transmission and behaves as a neuromodulator rather than as a "classical" neurotransmitter. In some cases 5-HT is co-localized in the same nerve terminal with other neurotransmitters and reciprocal interactions take place. This review will focus on the modulatory action of 5-HT on the effects of glutamate and gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA), which are the principal neurotransmitters mediating respectively excitatory and inhibitory signals in the CNS. Examples of interaction at pre-and/or post-synaptic levels will be illustrated, as well as the receptors involved and their mechanisms of action. Finally, the physiological meaning of neuromodulatory effects of 5-HT will be briefly discussed with respect to pathologies deriving from malfunctioning of serotonin system.
Keywords: GABA; Serotonin; cognition; glutamate; motor control; neuromodulation; nociception.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham WC, Bear MF. Metaplasticity: the plasticity of synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19(4):126–30. - PubMed
-
- Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ. Serotonin induces excitatory postsynaptic potentials in apical dendrites of neocortical pyramidal cells. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36(4-5):589–99. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Zoli M, Stromberg I, Fuxe K. Intercellular communication in the brain: wiring versus volume transmission. Neuroscience. 1995;69(3):711–26. - PubMed
-
- Ait Amara D, Segu L, Naili S, Buhot MC. Serotonin 1B receptor regulation after dorsal subiculum deafferentation. Brain Res Bull. 1995;38(1):17–23. - PubMed
-
- Andrade R, Chaput Y. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4-like receptors mediate the slow excitatory response to serotonin in the rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991;257(3):930–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
