Current experimental therapy for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 18615180
- PMCID: PMC2435347
- DOI: 10.2174/157015907780866901
Current experimental therapy for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
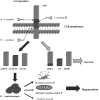
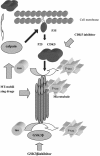
In the past decade, enormous efforts have been devoted to understand the genetics and molecular pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD), which has been transferred into extensive experimental approaches aimed at reversing disease progression. The trend in future AD therapy has been shifted from traditional anti-acetylcholinesterase treatment to multiple mechanisms-based therapy targeting amyloid plaques formation and amyloid peptides (Abeta)-mediated cytotoxicity, and neurofibrillary tangles generation. This review will cover current experimental studies with the focus on secretases-based drug development, immunotherapy, and anti-neurofibrillary tangles intervention. The outcome of these on-going studies may provide high hope that AD can be cured in the future.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Experimental approach; amyloid plaque; gene therapy; immunotherapy; neurofibrillary tangles; secretase; small interfering molecule.
Figures

References
-
- Adessi C, Frossard MJ, Boissard C, Fraga S, Bieler S, Ruckle T, Vilbois F, Robinson SM, Mutter M, Banks WA, Soto C. Pharmacological profiles of peptide drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13905–11. - PubMed
-
- Agdeppa ED, Kepe V, Liu J. 2-Dialkylamino-6- acylmalononitrile substituted naphthalenes (DDNP analogs): novel diagnostic and therapeutic tools in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Imaging Biol. 2003;5:404–17. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JJ, Holtz G, Baskin PP. Reductions in beta-amyloid concentrations in vivo by the gamma-secretase inhibitors BMS-289948 and BMS-299897. Biochem Pharmacol. 2005;69:689–98. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
