Dopamine, kidney, and hypertension: studies in dopamine receptor knockout mice
- PMID: 18615257
- PMCID: PMC3724362
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-008-0901-3
Dopamine, kidney, and hypertension: studies in dopamine receptor knockout mice
Abstract
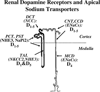
Dopamine is important in the pathogenesis of hypertension because of abnormalities in receptor-mediated regulation of renal sodium transport. Dopamine receptors are classified into D(1)-like (D(1), D(5)) and D(2)-like (D(2), D(3), D(4)) subtypes, all of which are expressed in the kidney. Mice deficient in specific dopamine receptors have been generated to provide holistic assessment on the varying physiological roles of each receptor subtype. This review examines recent studies on these mutant mouse models and evaluates the impact of individual dopamine receptor subtypes on blood pressure regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Hussain T, Lokhandwala MF. Renal dopamine receptors and hypertension. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2003;228:134–142. - PubMed
-
- Zeng C, Sanada H, Watanabe H, Eisner GM, Felder RA, Jose PA. Functional genomics of the dopaminergic system in hypertension. Physiol Genomics. 2004;19:233–246. - PubMed
-
- Dickson ME, Sigmund CD. Genetic basis of hypertension: revisiting angiotensinogen. Hypertension. 2006;48:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Osborn JW, Jacob F, Guzman P. A neural set point for the long-term control of arterial pressure: beyond the arterial baroreceptor reflex. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288:R846–R855. - PubMed
-
- Premont RT, Gainetdinov RR. Physiological roles of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and arrestins. Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;69:511–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

