Role of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) in gastrointestinal tract function and disease
- PMID: 18616431
- PMCID: PMC2705117
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20080022
Role of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) in gastrointestinal tract function and disease
Abstract
PPARbeta/delta (peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta) is one of three PPARs in the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that are collectively involved in the control of lipid homoeostasis among other functions. PPARbeta/delta not only acts as a ligand-activated transcription factor, but also affects signal transduction by interacting with other transcription factors such as NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB). Constitutive expression of PPARbeta/delta in the gastrointestinal tract is very high compared with other tissues and its potential physiological roles in this tissue include homoeostatic regulation of intestinal cell proliferation/differentiation and modulation of inflammation associated with inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. Analysis of mouse epithelial cells in the intestine and colon has clearly demonstrated that ligand activation of PPARbeta/delta induces terminal differentiation. The PPARbeta/delta target genes mediating this effect are currently unknown. Emerging evidence suggests that PPARbeta/delta can suppress inflammatory bowel disease through PPARbeta/delta-dependent and ligand-independent down-regulation of inflammatory signalling. However, the role of PPARbeta/delta in colon carcinogenesis remains controversial, as conflicting evidence suggests that ligand activation of PPARbeta/delta can either potentiate or attenuate this disease. In the present review, we summarize the role of PPARbeta/delta in gastrointestinal physiology and disease with an emphasis on findings in experimental models using both high-affinity ligands and null-mouse models.
Figures
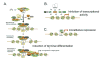
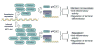

References
-
- Issemann I, Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990;347:645–650. - PubMed
-
- Grimaldi PA. Regulatory functions of PPARβ in metabolism: implications for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1771:983–990. - PubMed
-
- Ding G, Cheng L, Qin Q, Frontin S, Yang Q. PPARδ modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced TNFα inflammation signaling in cultured cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006;40:821–828. - PubMed
-
- Rival Y, Beneteau N, Taillandier T, et al. PPARα and PPARδ activators inhibit cytokine-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB and expression of VCAM-1 in EAhy926 endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;435:143–151. - PubMed
-
- Shan W, Nicol CJ, Ito S, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-β/δ protects against chemically induced liver toxicity in mice. Hepatology. 2008;47:225–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

