Nuclear and extranuclear pathway inputs in the regulation of global gene expression by estrogen receptors
- PMID: 18617595
- PMCID: PMC2631368
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0059
Nuclear and extranuclear pathway inputs in the regulation of global gene expression by estrogen receptors
Abstract
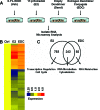
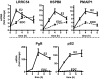
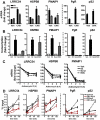
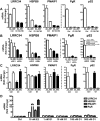
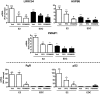
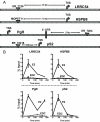
Whereas estrogens exert their effects by binding to nuclear estrogen receptors (ERs) and directly altering target gene transcription, they can also initiate extranuclear signaling through activation of kinase cascades. We have investigated the impact of estrogen-mediated extranuclear-initiated pathways on global gene expression by using estrogen-dendrimer conjugates (EDCs), which because of their charge and size remain outside the nucleus and can only initiate extranuclear signaling. Genome-wide cDNA microarray analysis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells identified a subset of 17beta-estradiol (E2)-regulated genes ( approximately 25%) as EDC responsive. The EDC and E2-elicited increases in gene expression were due to increases in gene transcription, as observed in nuclear run-on assays and RNA polymerase II recruitment and phosphorylation. Treatment with antiestrogen or ERalpha knockdown using small interfering RNA abolished EDC-mediated gene stimulation, whereas GPR30 knockdown or treatment with a GPR30-selective ligand was without effect, indicating ER as the mediator of these gene regulations. Inhibitors of MAPK kinase and c-Src suppressed both E2 and EDC stimulated gene expression. Of note, in chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, EDC was unable to recruit ERalpha to estrogen-responsive regions of regulated genes, whereas ERalpha recruitment by E2 was very effective. These findings suggest that other transcription factors or kinases that are downstream effectors of EDC-initiated extranuclear signaling cascades are recruited to regulatory regions of EDC-responsive genes in order to elicit gene stimulation. This study thus highlights the importance of inputs from both nuclear and extranuclear ER signaling pathways in regulating patterns of gene expression in breast cancer cells.
Figures
References
-
- Hall JM, Couse JF, Korach KS 2001 The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 276:36869–36872 - PubMed
-
- McDonnell DP, Norris JD 2002 Connections and regulation of the human estrogen receptor. Science 296:1642–1644 - PubMed
-
- Hammes SR, Levin ER 2007 Extranuclear steroid receptors: nature and actions. Endocr Rev 28:726–741 - PubMed
-
- Edwards DP 2005 Regulation of signal transduction pathways by estrogen and progesterone. Annu Rev Physiol 67:335–376 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

