Regulation of COX-2 expression and IL-6 release by particulate matter in airway epithelial cells
- PMID: 18617679
- PMCID: PMC5459547
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0105OC
Regulation of COX-2 expression and IL-6 release by particulate matter in airway epithelial cells
Abstract
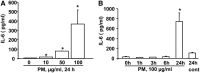
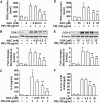
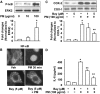
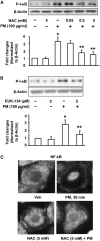
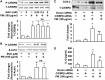
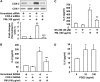
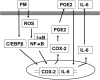
Particulate matter (PM) in ambient air is a risk factor for human respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. The delivery of PM to airway epithelial cells has been linked to release of proinflammatory cytokines; however, the mechanisms of PM-induced inflammatory responses are not well-characterized. This study demonstrates that PM induces cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression and IL-6 release through both a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent NF-kappaB pathway and an ROS-independent C/EBPbeta pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells (HBEpCs) in culture. Treatment of HBEpCs with Baltimore PM induced ROS production, COX-2 expression, and IL-6 release. Pretreatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) or EUK-134, in a dose-dependent manner, attenuated PM-induced ROS production, COX-2 expression, and IL-6 release. The PM-induced ROS was significantly of mitochondrial origin, as evidenced by increased oxidation of the mitochondrially targeted hydroethidine to hydroxyethidium by reaction with superoxide. Exposure of HBEpCs to PM stimulated phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta, while the NF-kappaB inhibitor, Bay11-7082, or C/EBPbeta siRNA attenuated PM-induced COX-2 expression and IL-6 release. Furthermore, NAC or EUK-134 attenuated PM-induced activation of NF-kappaB; however, NAC or EUK-134 had no effect on phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta. In addition, inhibition of COX-2 partly attenuated PM-induced Prostaglandin E2 and IL-6 release.
Figures




References
-
- Oberdorster G, Gelein RM, Ferin J, Weiss B. Association of particulate air pollution and acute mortality: involvement of ultrafine particles? Inhal Toxicol 1995;7:111–124. - PubMed
-
- Samet JM, Dominici F, Curriero FC, Coursac I, Zeger SL. Fine particulate air pollution and mortality in 20 US cities, 1987–1994. N Engl J Med 2000;343:1742–1749. - PubMed
-
- Dominici F, McDermott A, Zeger SL, Samet JM. Airborne particulate matter and mortality: timescale effects in four US cities. Am J Epidemiol 2003;157:1055–1065. - PubMed
-
- Samet JM, Krewski D. Health effects associated with exposure to ambient air pollution. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2007;70:227–242. - PubMed
-
- Sandstrom T. Respiratory effects of air pollutants: experimental studies in humans. Eur Respir J 1995;8:976–995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

