Severe Legionella pneumonia: rapid presumptive clinical diagnosis with Winthrop-University Hospital's weighted point score system (modified)
- PMID: 18620108
- PMCID: PMC7112393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2007.12.003
Severe Legionella pneumonia: rapid presumptive clinical diagnosis with Winthrop-University Hospital's weighted point score system (modified)
Erratum in
- Heart Lung. 2008 Sep-Oct;37(5):403
Abstract
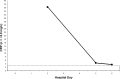
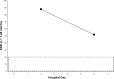
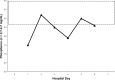
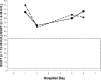
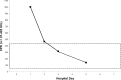
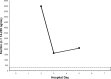
Legionnaires' disease is a systemic infection involving the lungs and accompanied by a characteristic pattern of extrapulmonary organ involvement. Legionnaires' disease is one of the non-zoonotic causes of atypical community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Legionnaires' disease commonly presents as severe CAP requiring hospitalization and intensive care. Each atypical CAP has its own characteristic pattern of extrapulmonary laboratory clinical findings and abnormalities that are the basis of clinical syndromic diagnosis. Studies have been unsuccessful in identifying individual clinical and laboratory parameters that are specific for Legionella. Individually, clinical and laboratory abnormalities lack diagnostic specificity. The diagnostic specificity of clinical and laboratory findings is increased when combined and are the basis of a clinical syndromic diagnosis. The importance of serial nonspecific laboratory abnormalities with Legionnaires' disease is emphasized. The sensitivity and specificity of a clinical syndromic diagnosis are enhanced if they are based on a weighted point score system. A diagnostic weighted point score system is based on the varying diagnostic importance of clinical and laboratory diagnostic findings. The Winthrop-University Hospital's Infectious Disease Division's rapid clinical diagnostic weighted point system is based on a weighted point score of clinical and laboratory findings. The case presented is that of a 55-year-old man with severe CAP who required hospitalization and intensive care admission. The presumptive clinical diagnosis of Legionella CAP was based on the Winthrop-University Hospital Infectious Disease Division's weighted point score system, which permitted early empiric anti-Legionella antimicrobial therapy and prompted specific Legionella testing. Legionnaires' disease is definitively diagnosed by serology or a urinary Legionella antigen test. This case of severe Legionnaires' CAP was confirmed by urinary antigen test reported on hospital day 6. The Winthrop-University Hospital is weighted point score system (modified) permits a rapid clinical presumptive diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease and is an accurate predictor of Legionella CAP.
Figures
References
-
- Kirby B.D., Synder K.M., Meyer R.D. Legionnaire's disease: clinical features of 24 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1978;89:297–309. - PubMed
-
- Cunha B.A., Quintiliani R. The atypical pneumonias, a diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Postgrad Med. 1979;66:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Cunha B.A., Ortega A.M. Atypical pneumonia: Extrapulmonary clues guide the way to diagnosis. Postgrad Med. 1966;99:123–128. - PubMed
-
- Johnson D.H., Cunha B.A. Clinical and extrapulmonary features of Chlamydia, mycoplasmas, and Legionella infections. Postgrad Med. 1992;93:69–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

