Comprehensive 3D-modeling of allergenic proteins and amino acid composition of potential conformational IgE epitopes
- PMID: 18621419
- PMCID: PMC2593650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.05.026
Comprehensive 3D-modeling of allergenic proteins and amino acid composition of potential conformational IgE epitopes
Abstract
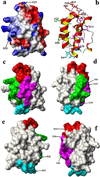
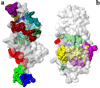
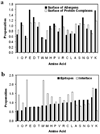
Similarities in sequences and 3D structures of allergenic proteins provide vital clues to identify clinically relevant immunoglobulin E (IgE) cross-reactivities. However, experimental 3D structures are available in the Protein Data Bank for only 5% (45/829) of all allergens catalogued in the Structural Database of Allergenic Proteins (SDAP, http://fermi.utmb.edu/SDAP). Here, an automated procedure was used to prepare 3D-models of all allergens where there was no experimentally determined 3D structure or high identity (95%) to another protein of known 3D structure. After a final selection by quality criteria, 433 reliable 3D models were retained and are available from our SDAP Website. The new 3D models extensively enhance our knowledge of allergen structures. As an example of their use, experimentally derived "continuous IgE epitopes" were mapped on 3 experimentally determined structures and 13 of our 3D-models of allergenic proteins. Large portions of these continuous sequences are not entirely on the surface and therefore cannot interact with IgE or other proteins. Only the surface exposed residues are constituents of "conformational IgE epitopes" which are not in all cases continuous in sequence. The surface exposed parts of the experimental determined continuous IgE epitopes showed a distinct statistical distribution as compared to their presence in typical protein-protein interfaces. The amino acids Ala, Ser, Asn, Gly and particularly Lys have a high propensity to occur in IgE binding sites. The 3D-models will facilitate further analysis of the common properties of IgE binding sites of allergenic proteins.
Figures
References
-
- Aalberse RC, Stadler BM. In silico predictability of allergenicity: From amino acid sequence via 3-D structure to allergenicity:. From amino acid sequence via 3-D structure to allergenicity. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 2006;50:625–627. - PubMed
-
- Asturias JA, Gomez-Bayon N, Eseverri JL, Martinez A. Par j 1 and Par j 2, the major allergens from Parietaria judaica pollen, have similar immunoglobulin E epitopes. Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 2003;33:518–524. - PubMed
-
- Bannon G, Cockrell G, Connaughton C, West CM, Helm R, Stanley JS, King N, Rabjohn P, Sampson HA, Burks AW. Engineering, characterization and in vitro efficacy of the major peanut allergens for use in immunotherapy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001;124:70–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

