Interplay of unsaturated phospholipids and cholesterol in membranes: effect of the double-bond position
- PMID: 18621818
- PMCID: PMC2547435
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.108.138123
Interplay of unsaturated phospholipids and cholesterol in membranes: effect of the double-bond position
Abstract
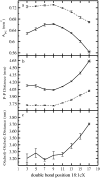
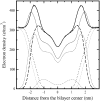
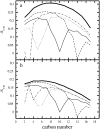
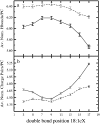
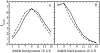
The structural and dynamical properties of lipid membranes rich in phospholipids and cholesterol are known to be strongly affected by the unsaturation of lipid acyl chains. We show that not only unsaturation but also the position of a double bond has a pronounced effect on membrane properties. We consider how cholesterol interacts with phosphatidylcholines comprising two 18-carbon long monounsaturated acyl chains, where the position of the double bond is varied systematically along the acyl chains. Atomistic molecular dynamics simulations indicate that when the double bond is not in contact with the cholesterol ring, and especially with the C18 group on its rough beta-side, the membrane properties are closest to those of the saturated bilayer. However, any interaction between the double bond and the ring promotes membrane disorder and fluidity. Maximal disorder is found when the double bond is located in the middle of a lipid acyl chain, the case most commonly found in monounsaturated acyl chains of phospholipids. The results suggest a cholesterol-mediated lipid selection mechanism in eukaryotic cell membranes. With saturated lipids, cholesterol promotes the formation of highly ordered raft-like membrane domains, whereas domains rich in unsaturated lipids with a double bond in the middle remain highly fluid despite the presence of cholesterol.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Is a fluid-mosaic model of biological membranes fully relevant? Studies on lipid organization in model and biological membranes.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2003;8(1):147-59. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2003. PMID: 12655369
-
Effect of the structure of lipids favoring disordered domain formation on the stability of cholesterol-containing ordered domains (lipid rafts): identification of multiple raft-stabilization mechanisms.Biophys J. 2007 Dec 15;93(12):4307-18. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.114967. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17766350 Free PMC article.
-
Why is the sn-2 chain of monounsaturated glycerophospholipids usually unsaturated whereas the sn-1 chain is saturated? Studies of 1-stearoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (SOPC) and 1-oleoyl-2-stearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (OSPC) membranes with and without cholesterol.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Jun 18;113(24):8347-56. doi: 10.1021/jp902131b. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19469492
-
Dynamics of raft molecules in the cell and artificial membranes: approaches by pulse EPR spin labeling and single molecule optical microscopy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Mar 10;1610(2):231-43. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(03)00021-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12648777 Review.
-
Defining raft domains in the plasma membrane.Traffic. 2020 Jan;21(1):106-137. doi: 10.1111/tra.12718. Traffic. 2020. PMID: 31760668 Review.
Cited by
-
Varying the position of phospholipid acyl chain unsaturation modulates hopanoid and sterol ordering.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 9:2023.09.06.556521. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.06.556521. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biophys J. 2024 Jul 2;123(13):1896-1902. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.06.002. PMID: 38370701 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Studying interfacial reactions of cholesterol sulfate in an unsaturated phosphatidylglycerol layer with ozone using field induced droplet ionization mass spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2012 Jan;23(1):141-52. doi: 10.1007/s13361-011-0275-9. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2012. PMID: 22069038
-
Mass Spectrometry Imaging with Isomeric Resolution Enabled by Ozone-Induced Dissociation.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Aug 13;57(33):10530-10534. doi: 10.1002/anie.201802937. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29787633 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Metabolism Interplay in CRC-An Update.Metabolites. 2022 Feb 26;12(3):213. doi: 10.3390/metabo12030213. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35323656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From cholesterogenesis to steroidogenesis: role of riboflavin and flavoenzymes in the biosynthesis of vitamin D.Adv Nutr. 2014 Mar 1;5(2):144-63. doi: 10.3945/an.113.005181. Adv Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24618756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mouritsen, O. G. 2005. Life—As a Matter of Fat. Springer, Berlin.
-
- Ikonen, E. 2006. Mechanisms for cellular cholesterol transport: defects and human disease. Physiol. Rev. 86:1237–1261. - PubMed
-
- Simons, K., and E. Ikonen. 1997. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 387:569–572. - PubMed
-
- Brown, D. A., and E. London. 1998. Functions of lipid rafts in biological membranes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 14:111–136. - PubMed
-
- Munro, S. 2003. Lipid rafts: elusive or illusive? Cell 115:377–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

