Chronic intrauterine pulmonary hypertension increases endothelial cell Rho kinase activity and impairs angiogenesis in vitro
- PMID: 18621906
- PMCID: PMC2575951
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00516.2007
Chronic intrauterine pulmonary hypertension increases endothelial cell Rho kinase activity and impairs angiogenesis in vitro
Abstract
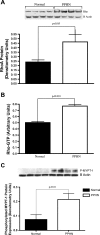
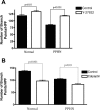
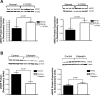
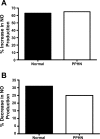
Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) is characterized by endothelial dysfunction and decreased vascular growth. The role of Rho kinase activity in modulating endothelial function and regulating angiogenesis during normal lung development and in PPHN is unknown. We hypothesized that PPHN increases Rho kinase activity in fetal pulmonary artery endothelial cells (PAECs) and impairs angiogenesis in vitro. Proximal PAECs were harvested from fetal sheep with partial ligation of the ductus arteriosus in utero (PPHN) and age-matched controls. Rho kinase activity was measured by RhoA, Rho GTP, and phosphorylated MYPT-1 protein content. The effects of Rho kinase activity on angiogenesis, endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase (eNOS) protein expression, and NO production were determined in normal and PPHN PAECs. Angiogenesis was assessed by tube formation in vitro with/without Y-27632 (a Rho kinase inhibitor) and calpeptin (a Rho kinase activator) in the presence/absence of N-nitro-l-arginine (l-NA, an NOS inhibitor). RhoA, Rho GTP, and phosphorylated MYPT-1 protein were increased in PPHN PAECs. Tube formation was reduced 29% in PPHN PAECs (P < 0.001) and increased with Y-27632 treatment in normal and PPHN PAECs, with PPHN PAECs achieving levels similar to those of normal PAECs. l-NA inhibited the Y-27632-induced increase in tube formation in normal, but not PPHN, PAECs. Calpeptin reduced tube formation in normal and PPHN PAECs. eNOS expression was reduced 42% in PPHN PAECs (P < 0.01). Y-27632 increased eNOS protein and NO production in normal and PPHN PAECs. Calpeptin decreased eNOS protein only in normal PAECs but reduced NO production in normal and PPHN PAECs. We conclude that Rho kinase activity is increased in PPHN PAECs and impairs angiogenesis and downregulates eNOS protein and NO production in vitro.
Figures



References
-
- Arbajal JM, Schaeffer RC Jr. RhoA inactivation enhances endothelial cell barrier function. RhoA inactivation enhances endothelial cell barrier function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 277: C955–C964, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Belik J, Keeley FW, Baldwin F, Rabinovitch M. Pulmonary hypertension and vascular remodeling in fetal sheep. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 266: H2303–H2309, 1994. - PubMed
-
- Bi D, Nishimura J, Niiro N, Hirano K, Kanaide H. Contractile properties of the cultured vascular smooth muscle cells: the crucial role played by RhoA in the regulation of contractility. Circ Res 96: 890–897, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Bussemaker E, Pistrosch F, Forrster S, Herbrig K, Gross P, Passauer J, Brandes RP. Rho kinase contributes to basal vascular tone in humans: role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293: H541–H547, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

