Identity-by-descent estimation and mapping of qualitative traits in large, complex pedigrees
- PMID: 18622032
- PMCID: PMC2475756
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.108.089912
Identity-by-descent estimation and mapping of qualitative traits in large, complex pedigrees
Abstract
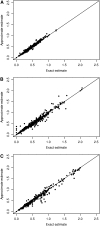
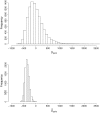
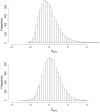
Computing identity-by-descent sharing between individuals connected through a large, complex pedigree is a computationally demanding task that often cannot be done using exact methods. What I present here is a rapid computational method for estimating, in large complex pedigrees, the probability that pairs of alleles are IBD given the single-point genotype data at that marker for all individuals. The method can be used on pedigrees of essentially arbitrary size and complexity without the need to divide the individuals into separate subpedigrees. I apply the method to do qualitative trait linkage mapping using the nonparametric sharing statistic S(pairs). The validity of the method is demonstrated via simulation studies on a 13-generation 3028-person pedigree with 700 genotyped individuals. An analysis of an asthma data set of individuals in this pedigree finds four loci with P-values <10(-3) that were not detected in prior analyses. The mapping method is fast and can complete analyses of approximately 150 affected individuals within this pedigree for thousands of markers in a matter of hours.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identity by descent estimation with dense genome-wide genotype data.Genet Epidemiol. 2011 Sep;35(6):557-67. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20606. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Genet Epidemiol. 2011. PMID: 21769932 Free PMC article.
-
Multipoint quantitative-trait linkage analysis in general pedigrees.Am J Hum Genet. 1998 May;62(5):1198-211. doi: 10.1086/301844. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. PMID: 9545414 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of pedigree complexity on quantitative trait linkage analysis.Genet Epidemiol. 2001;21 Suppl 1:S236-43. doi: 10.1002/gepi.2001.21.s1.s236. Genet Epidemiol. 2001. PMID: 11793675
-
Estimating genealogies from unlinked marker data: a Bayesian approach.Theor Popul Biol. 2007 Nov;72(3):305-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2007.06.004. Epub 2007 Jun 22. Theor Popul Biol. 2007. PMID: 17681576 Review.
-
QTL analysis in arbitrary pedigrees with incomplete marker information.Heredity (Edinb). 2002 Nov;89(5):339-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800136. Heredity (Edinb). 2002. PMID: 12399991 Review.
Cited by
-
A system for exact and approximate genetic linkage analysis of SNP data in large pedigrees.Bioinformatics. 2013 Jan 15;29(2):197-205. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts658. Epub 2012 Nov 18. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23162081 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide association analysis in a mouse advanced intercross line.Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 4;9(1):5162. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07642-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30514929 Free PMC article.
-
Genealogical analysis as a new approach for the investigation of drug intolerance heritability.Eur J Hum Genet. 2014 Jul;22(7):916-22. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.270. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24281370 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Genes and quantitative genetic variation involved with senescence in cells, organs, and the whole plant.Front Genet. 2015 Feb 23;6:57. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00057. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25755664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identity by descent estimation with dense genome-wide genotype data.Genet Epidemiol. 2011 Sep;35(6):557-67. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20606. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Genet Epidemiol. 2011. PMID: 21769932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abecasis, G. R., S. S. Cherny, W. O. Cookson and L. R. Cardon, 2002. Merlin–rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat. Genet. 30 97–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

