A polymorphism of G-protein coupled receptor kinase5 alters agonist-promoted desensitization of beta2-adrenergic receptors
- PMID: 18622265
- PMCID: PMC2699179
- DOI: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e32830967e9
A polymorphism of G-protein coupled receptor kinase5 alters agonist-promoted desensitization of beta2-adrenergic receptors
Abstract
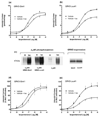
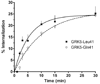
Beta-agonist treatment of asthma displays substantial interindividual variation, which has prompted polymorphism discovery and characterization of beta2-adrenergic (beta2AR) signaling genes. beta2AR function undergoes desensitization during persistent agonist exposure because of receptor phosphorylation by G-protein coupled receptor kinases (GRKs). GRK5 was found to be highly expressed in airway smooth muscle, the tissue target for beta-agonists. The coding region is polymorphic at codon 41, where Gln can be substituted by Leu (minor allele), but almost exclusively in those of African descent. In transfected cells, GRK5-Leu41 evoked a greater degree of agonist-promoted desensitization of adenylyl cyclase compared with GRK5-Gln41. Consistent with this functional effect, agonist-promoted beta2AR phosphorylation was greater in cells expressing GRK5-Leu41, as was the rate of agonist-promoted receptor internalization. In studies with mutated beta2AR lacking PKA-phosphorylation sites, this phenotype was confirmed as being GRK-specific. So, GRK5-Leu41 represents a gain-of-function polymorphism that evokes enhanced loss-of-function of beta2AR during persistent agonist exposure, and thus may contribute to beta-agonist variability in asthma treatment of African-Americans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeted transgenesis reveals discrete attenuator functions of GRK and PKA in airway beta2-adrenergic receptor physiologic signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 1;106(35):15007-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906034106. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19706446 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the beta2-adrenergic receptor in plasma membranes by intrinsic GRK5.Biochemistry. 2007 Dec 18;46(50):14438-49. doi: 10.1021/bi700922h. Epub 2007 Nov 23. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 18034461
-
Characterization of agonist stimulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and G protein-coupled receptor kinase phosphorylation of the beta2-adrenergic receptor using phosphoserine-specific antibodies.Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Jan;65(1):196-206. doi: 10.1124/mol.65.1.196. Mol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14722251
-
A GRK5 polymorphism that inhibits beta-adrenergic receptor signaling is protective in heart failure.Nat Med. 2008 May;14(5):510-7. doi: 10.1038/nm1750. Epub 2008 Apr 20. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18425130 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of β2-adrenoceptor and adenosine A2B receptor signalling by GRK and arrestin proteins in arterial smooth muscle.Cell Signal. 2018 Nov;51:86-98. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.07.013. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30075183
Cited by
-
G protein receptor kinase 4 polymorphisms: β-blocker pharmacogenetics and treatment-related outcomes in hypertension.Hypertension. 2012 Oct;60(4):957-64. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.198721. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Hypertension. 2012. PMID: 22949529 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted transgenesis reveals discrete attenuator functions of GRK and PKA in airway beta2-adrenergic receptor physiologic signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 1;106(35):15007-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906034106. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19706446 Free PMC article.
-
Novel inhibitors of phosphorylation independent activity of GRK2 modulate cAMP signaling.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022 Apr;10(2):e00913. doi: 10.1002/prp2.913. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022. PMID: 35184416 Free PMC article.
-
Potential genetic risk factors for chronic TMD: genetic associations from the OPPERA case control study.J Pain. 2011 Nov;12(11 Suppl):T92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2011.08.005. J Pain. 2011. PMID: 22074755 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic Structure of GRK5 Reveals Distinct Structural Features Novel for G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinases.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 21;290(34):20629-20647. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.647297. Epub 2015 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26032409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liggett SB, Green SA. Molecular Biology of the β2-adrenergic receptor: Focus on Interactions of Agonist with Receptor. In: Pauwels R, Lofdahl CG, O'Byrne P, editors. Beta2- Agonists in Asthma Treatment. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 1996. pp. 19–34.
-
- Tran TM, Jorgensen R, Clark RB. Phosphorylation of the beta2-adrenergic receptor in plasma membranes by intrinsic GRK5. Biochem. 2007;46:14438–14449. - PubMed
-
- Violin JD, Ren XR, Lefkowitz RJ. G-protein-coupled receptor kinase specificity for beta-arrestin recruitment to the beta2-adrenergic receptor revealed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:20577–20588. - PubMed
-
- Lipworth BJ. Airway subsensitivity with long-acting beta 2-agonists. Is there cause for concern? Drug Saf. 1997;16:295–308. - PubMed
-
- Drazen JM, Silverman EK, Lee TH. Heterogeneity of therapeutic responses in asthma. Br Med Bull. 2000;56:1054–1070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

