An in silico analysis of T-box regulated genes and T-box evolution in prokaryotes, with emphasis on prediction of substrate specificity of transporters
- PMID: 18625071
- PMCID: PMC2494555
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-330
An in silico analysis of T-box regulated genes and T-box evolution in prokaryotes, with emphasis on prediction of substrate specificity of transporters
Abstract
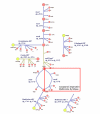
Background: T-box anti-termination is an elegant and sensitive mechanism by which many bacteria maintain constant levels of amino acid-charged tRNAs. The amino acid specificity of the regulatory element is related to a so-called specifier codon and can in principle be used to guide the functional annotation of the genes controlled via the T-box anti-termination mechanism.
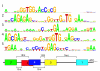
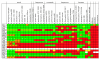
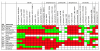
Results: Hidden Markov Models were defined to search the T-box regulatory element and were applied to all completed prokaryotic genomes. The vast majority of the genes found downstream of the retrieved elements encoded functionalities related to transport and synthesis of amino acids and the charging of tRNA. This is completely in line with findings reported in literature and with the proposed biological role of the regulatory element. For several species, the functional annotation of a large number of genes encoding proteins involved in amino acid transport could be improved significantly on basis of the amino acid specificity of the identified T-boxes. In addition, these annotations could be extrapolated to a larger number of orthologous systems in other species. Analysis of T-box distribution confirmed that the element is restricted predominantly to species of the phylum Firmicutes. Furthermore, it appeared that the distribution was highly species specific and that in the case of amino acid transport some boxes seemed to "pop-up" only recently.
Conclusion: We have demonstrated that the identification of the molecular specificity of a regulatory element can be of great help in solving notoriously difficult annotation issues, e.g. by defining the substrate specificity of genes encoding amino acid transporters on basis of the amino acid specificity of the regulatory T-box. Furthermore, our analysis of the species-dependency of the occurrence of specific T-boxes indicated that these regulatory elements propagate in a semi-independent way from the genes that they control.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biochemical features and functional implications of the RNA-based T-box regulatory mechanism.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Mar;73(1):36-61. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00026-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19258532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of T-box regulatory systems in bacteria.RNA. 2008 Apr;14(4):717-35. doi: 10.1261/rna.819308. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18359782 Free PMC article.
-
The T box regulatory element controlling expression of the class I lysyl-tRNA synthetase of Bacillus cereus strain 14579 is functional and can be partially induced by reduced charging of asparaginyl-tRNAAsn.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Jul 22;10:196. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-196. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20649968 Free PMC article.
-
Premature terminator analysis sheds light on a hidden world of bacterial transcriptional attenuation.Genome Biol. 2010;11(9):R97. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-9-r97. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20920266 Free PMC article.
-
T-box genes in development: from hydra to humans.Int Rev Cytol. 2001;207:1-70. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(01)07002-4. Int Rev Cytol. 2001. PMID: 11352264 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of branched-chain amino acid transport in Bacillus subtilis CodY activity.J Bacteriol. 2015 Apr;197(8):1330-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.02563-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25645558 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-induced changes in T box antiterminator RNA stability.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2012 Feb;79(2):202-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01274.x. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2012. PMID: 22117759 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical features and functional implications of the RNA-based T-box regulatory mechanism.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Mar;73(1):36-61. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00026-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19258532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic engineering of branch chain amino acid supply modules for the enhanced production of bacitracin from Bacillus licheniformis.Metab Eng Commun. 2020 Jun 11;11:e00136. doi: 10.1016/j.mec.2020.e00136. eCollection 2020 Dec. Metab Eng Commun. 2020. PMID: 32637317 Free PMC article.
-
Complete resequencing and reannotation of the Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 genome.J Bacteriol. 2012 Jan;194(1):195-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.06275-11. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22156394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schilling O, Langbein I, Muller M, Schmalisch MH, Stulke J. A protein-dependent riboswitch controlling ptsGHI operon expression in Bacillus subtilis: RNA structure rather than sequence provides interaction specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:2853–2864. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh611. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

