IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 18625622
- PMCID: PMC3811149
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2008.092932
IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial
Erratum in
- Ann Rheum Dis. 2009 Feb;68(2):296
Abstract
Objectives: The phase III RADIATE study examined the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) refractory to tumour necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist therapy.
Methods: 499 patients with inadequate response to one or more TNF antagonists were randomly assigned to receive 8 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg tocilizumab or placebo (control) intravenously every 4 weeks with stable methotrexate for 24 weeks. ACR20 responses, secondary efficacy and safety endpoints were assessed.
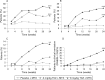
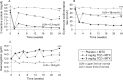
Results: ACR20 was achieved at 24 weeks by 50.0%, 30.4% and 10.1% of patients in the 8 mg/kg, 4 mg/kg and control groups, respectively (less than p<0.001 both tocilizumab groups versus control). At week 4 more patients achieved ACR20 in 8 mg/kg tocilizumab versus controls (less than p = 0.001). Patients responded regardless of most recently failed anti-TNF or the number of failed treatments. DAS28 remission (DAS28 <2.6) rates at week 24 were clearly dose related, being achieved by 30.1%, 7.6% and 1.6% of 8 mg/kg, 4 mg/kg and control groups (less than p = 0.001 for 8 mg/kg and p = 0.053 for 4 mg/kg versus control). Most adverse events were mild or moderate with overall incidences of 84.0%, 87.1% and 80.6%, respectively. The most common adverse events with higher incidence in tocilizumab groups were infections, gastrointestinal symptoms, rash and headache. The incidence of serious adverse events was higher in controls (11.3%) than in the 8 mg/kg (6.3%) and 4 mg/kg (7.4%) groups.
Conclusion: Tocilizumab plus methotrexate is effective in achieving rapid and sustained improvements in signs and symptoms of RA in patients with inadequate response to TNF antagonists and has a manageable safety profile.
Trial registration number: NCT00106522.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
When patients with rheumatoid arthritis fail tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: what is the next step?Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Nov;67(11):1497-8. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.098111. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 18854512 No abstract available.
-
RADIATE: more treatment options for patients with an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor antagonists.Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2009 Feb;5(2):66-7. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0984. Epub 2008 Dec 23. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19107112
References
-
- Gabriel SE. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2001;27:269–81 - PubMed
-
- Vander Cruyssen B, Van Looy S, Wyns B, Westhovens R, Durez P, Van den Bosch F, et al. Four-year follow-up of infliximab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients with long-standing refractory disease: attrition and long-term evolution of disease activity. Arthritis Res Ther 2006;8:R112 doi:10.1186/ar2001. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kremer JM. Rational use of new and existing disease-modifying agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 2001;134:695–706 - PubMed
-
- Shankar S, Handa R. Biological agents in rheumatoid arthritis. J Postgrad Med 2004;50:293–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

