Discriminating gene expression profiles of memory B cell subpopulations
- PMID: 18625746
- PMCID: PMC2525601
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20072682
Discriminating gene expression profiles of memory B cell subpopulations
Abstract
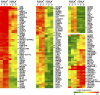
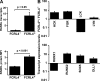
Morphologically and functionally distinct subpopulations of human memory B (B(Mem)) cells are identifiable by either their expression of CD27 or Fc receptor-like 4 (FCRL4), an immunoglobulin domain containing a receptor with strong inhibitory potential. We have conducted comparative transcriptome and proteome analyses of FCRL4(+) and FCRL4(-) B(Mem) cells and found that these two subsets have very distinctive expression profiles for genes encoding transcription factors, cell-surface proteins, intracellular signaling molecules, and modifiers of the cell-cycle status. Among the differentially expressed transcription factors, runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) transcript levels were up-regulated in FCRL4(-) cells, whereas RUNX2 transcripts were preferentially detected in FCRL4(+) cells. In vitro evidence for FCRL4 promoter responsiveness and in vivo promoter occupancy suggested that RUNX transcription factors are involved in the generation of these B(Mem) cell subpopulations. A distinctive signature profile was defined for the FCRL4(+) B(Mem) cells by their expression of CD11c, receptor activator for nuclear factor kappaB ligand, and FAS cell-surface proteins, in combination with increased levels of SOX5, RUNX2, DLL1, and AICDA expression. We conclude that this recently identified subpopulation of B(Mem) cells, which normally resides in epithelial tissue-based niches, may serve a unique role in mucosal defense and, conversely, as a target for neoplastic transformation events.
Figures




References
-
- Crotty, S., and R. Ahmed. 2004. Immunological memory in humans. Semin. Immunol. 16:197–203. - PubMed
-
- Dorner, T., and A. Radbruch. 2007. Antibodies and B cell memory in viral immunity. Immunity. 27:384–392. - PubMed
-
- Klein, U., K. Rajewsky, and R. Kuppers. 1998. Human immunoglobulin (Ig)M+IgD+ peripheral blood B cells expressing the CD27 cell surface antigen carry somatically mutated variable region genes: CD27 as a general marker for somatically mutated (memory) B cells. J. Exp. Med. 188:1679–1689. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agematsu, K., H. Nagumo, F.C. Yang, T. Nakazawa, K. Fukushima, S. Ito, K. Sugita, T. Mori, T. Kobata, C. Morimoto, and A. Komiyama. 1997. B cell subpopulations separated by CD27 and crucial collaboration of CD27+ B cells and helper T cells in immunoglobulin production. Eur. J. Immunol. 27:2073–2079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

