In vitro and in vivo treatments of echinococcus protoscoleces and metacestodes with artemisinin and artemisinin derivatives
- PMID: 18625777
- PMCID: PMC2533465
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00553-08
In vitro and in vivo treatments of echinococcus protoscoleces and metacestodes with artemisinin and artemisinin derivatives
Abstract
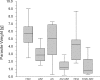
In vitro treatment of Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus granulosus larval stages with the antimalarials dihydroartemisinin and artesunate (10 to 40 microM) exhibited promising results, while 6 weeks of in vivo treatment of mice infected with E. multilocularis metacestodes (200 mg/kg of body weight/day) had no effect. However, combination treatments of both drugs with albendazole led to a substantial but statistically not significant reduction in parasite weight compared to results with albendazole alone.
Figures


References
-
- Avery, M. A., K. M. Muraleedharan, P. V. Desai, A. K. Bandyopadhyaya, M. M. Furtado, and B. L. Tekwani. 2003. Structure-activity relationships of the antimalarial agent artemisinin. Design, synthesis, and CoMFA studies toward the development of artemisinin-based drugs against leishmaniasis and malaria. J. Med. Chem. 46:4244-4258. - PubMed
-
- Golenser, J., J. H. Waknine, M. Krugliak, N. H. Hunt, and G. E. Grau. 2006. Current perspectives on the mechanism of action of artemisinins. Int. J. Parasitol. 36:1427-1441. - PubMed
-
- Gordi, T., and E. I. Lepist. 2004. Artemisinin derivatives: toxic for laboratory animals, safe for humans? Toxicology Lett. 147:99-107. - PubMed
-
- Gottstein, B., and A. Hemphill. 14 March 2008, posting date. The host-parasite interplay. Exp. Parasitol. 119:447-452. [Epub ahead of print.] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

