Microsatellites as EWS/FLI response elements in Ewing's sarcoma
- PMID: 18626011
- PMCID: PMC2481306
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801073105
Microsatellites as EWS/FLI response elements in Ewing's sarcoma
Abstract
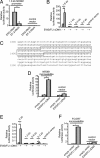
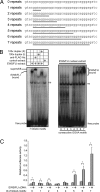
The ETS gene family is frequently involved in chromosome translocations that cause human cancer, including prostate cancer, leukemia, and sarcoma. However, the mechanisms by which oncogenic ETS proteins, which are DNA-binding transcription factors, target genes necessary for tumorigenesis is not well understood. Ewing's sarcoma serves as a paradigm for the entire class of ETS-associated tumors because nearly all cases harbor recurrent chromosomal translocations involving ETS genes. The most common translocation in Ewing's sarcoma encodes the EWS/FLI oncogenic transcription factor. We used whole genome localization (ChIP-chip) to identify target genes that are directly bound by EWS/FLI. Analysis of the promoters of these genes demonstrated a significant over-representation of highly repetitive GGAA-containing elements (microsatellites). In a parallel approach, we found that EWS/FLI uses GGAA microsatellites to regulate the expression of some of its target genes including NR0B1, a gene required for Ewing's sarcoma oncogenesis. The microsatellite in the NR0B1 promoter bound EWS/FLI in vitro and in vivo and was both necessary and sufficient to confer EWS/FLI regulation to a reporter gene. Genome wide computational studies demonstrated that GGAA microsatellites were enriched close to EWS/FLI-up-regulated genes but not down-regulated genes. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that the ability of EWS/FLI to bind DNA and modulate gene expression through these repetitive elements depended on the number of consecutive GGAA motifs. These findings illustrate an unprecedented route to specificity for ETS proteins and use of microsatellites in tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nunn MF, Seeburg PH, Moscovici C, Duesberg PH. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983;306:391–395. - PubMed
-
- de Taisne C, Gegonne A, Stehelin D, Bernheim A, Berger R. Chromosomal localization of the human proto-oncogene c-ets. Nature. 1984;310:581–583. - PubMed
-
- Seth A, Watson DK. ETS transcription factors and their emerging roles in human cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:2462–2478. - PubMed
-
- Tomlins SA, et al. TMPRSS2:ETV4 gene fusions define a third molecular subtype of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3396–3400. - PubMed
-
- Tomlins SA, et al. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 2005;310:644–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

