Conserved T cell receptor alpha-chain induces insulin autoantibodies
- PMID: 18626021
- PMCID: PMC2464615
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801648105
Conserved T cell receptor alpha-chain induces insulin autoantibodies
Abstract
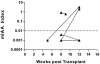
A fundamental question is what are the molecular determinants that lead to spontaneous preferential targeting of specific autoantigens in autoimmune diseases, such as the insulin B:9-23 peptide sequence in type 1 diabetes. Anti-insulin B:9-23 T cell clones isolated from prediabetic NOD islets have a conserved Valpha-segment/Jalpha-segment, but no conservation of the alpha-chain N region and no conservation of the Vbeta-chain. Here, we show that the conserved T cell receptor alpha-chain generates insulin autoantibodies when transgenically or retrogenically introduced into mice without its corresponding Vbeta. We suggest that a major part of the mystery as to why islet autoimmunity develops relates to recognition of a primary insulin peptide by a conserved alpha chain T cell receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




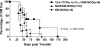
Similar articles
-
Islet-associated T-cell receptor-β CDR sequence repertoire in prediabetic NOD mice reveals antigen-driven T-cell expansion and shared usage of VβJβ TCR chains.Mol Immunol. 2015 Mar;64(1):127-35. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.11.009. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25480393
-
Restricted islet-cell reactive T cell repertoire of early pancreatic islet infiltrates in NOD mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jul 9;99(14):9374-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.142284899. Epub 2002 Jun 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12082183 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells generated in response to insulin B:9-23 peptide prevent adoptive transfer of diabetes by diabetogenic T cells.J Autoimmun. 2003 Nov;21(3):221-37. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(03)00114-8. J Autoimmun. 2003. PMID: 14599847
-
Type I diabetes mellitus: a predictable autoimmune disease with interindividual variation in the rate of beta cell destruction.Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Jan;50(1 Pt 2):S85-95. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90115-3. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989. PMID: 2642771 Review.
-
Diabetogenic T-cell clones.Diabetes. 1996 Oct;45(10):1299-305. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.10.1299. Diabetes. 1996. PMID: 8826963 Review.
Cited by
-
T-cell receptor retrogenic mice: a rapid, flexible alternative to T-cell receptor transgenic mice.Immunology. 2012 Jul;136(3):265-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03574.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22348644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal antibody blocking the recognition of an insulin peptide-MHC complex modulates type 1 diabetes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 18;111(7):2656-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323436111. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24550292 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy in autoimmune type 1 diabetes.Rev Diabet Stud. 2012 Summer-Fall;9(2-3):68-81. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2012.9.68. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Rev Diabet Stud. 2012. PMID: 23403703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specificity and detection of insulin-reactive CD4+ T cells in type 1 diabetes in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Oct 4;108(40):16729-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113954108. Epub 2011 Sep 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21949373 Free PMC article.
-
Treg vaccination with a strong-agonistic insulin mimetope.Curr Diab Rep. 2012 Oct;12(5):463-70. doi: 10.1007/s11892-012-0295-2. Curr Diab Rep. 2012. PMID: 22763731 Review.
References
-
- Lieberman SM, DiLorenzo TP. A comprehensive guide to antibody and T-cell responses in type 1 diabetes. Tissue Antigens. 2003;62:359–377. - PubMed
-
- Jaeckel E, Lipes MA, von Boehmer H. Recessive tolerance to preproinsulin 2 reduces but does not abolish type 1 diabetes. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:1028–1035. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

