Conserved T cell receptor alpha-chain induces insulin autoantibodies
- PMID: 18626021
- PMCID: PMC2464615
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801648105
Conserved T cell receptor alpha-chain induces insulin autoantibodies
Abstract
A fundamental question is what are the molecular determinants that lead to spontaneous preferential targeting of specific autoantigens in autoimmune diseases, such as the insulin B:9-23 peptide sequence in type 1 diabetes. Anti-insulin B:9-23 T cell clones isolated from prediabetic NOD islets have a conserved Valpha-segment/Jalpha-segment, but no conservation of the alpha-chain N region and no conservation of the Vbeta-chain. Here, we show that the conserved T cell receptor alpha-chain generates insulin autoantibodies when transgenically or retrogenically introduced into mice without its corresponding Vbeta. We suggest that a major part of the mystery as to why islet autoimmunity develops relates to recognition of a primary insulin peptide by a conserved alpha chain T cell receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




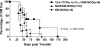
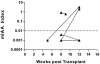
References
-
- Lieberman SM, DiLorenzo TP. A comprehensive guide to antibody and T-cell responses in type 1 diabetes. Tissue Antigens. 2003;62:359–377. - PubMed
-
- Jaeckel E, Lipes MA, von Boehmer H. Recessive tolerance to preproinsulin 2 reduces but does not abolish type 1 diabetes. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:1028–1035. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

