Human DDX3 functions in translation and interacts with the translation initiation factor eIF3
- PMID: 18628297
- PMCID: PMC2504307
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn454
Human DDX3 functions in translation and interacts with the translation initiation factor eIF3
Abstract
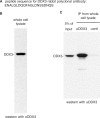
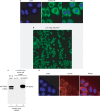
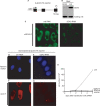
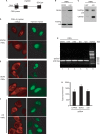
The conserved RNA helicase DDX3 is of major medical importance due to its involvement in numerous cancers, human hepatitis C virus (HCV) and HIV. Although DDX3 has been reported to have a wide variety of cellular functions, its precise role remains obscure. Here, we raised a new antibody to DDX3 and used it to show that DDX3 is evenly distributed throughout the cytoplasm at steady state. Consistent with this observation, HA-tagged DDX3 also localizes to the cytoplasm. RNAi of DDX3 in both human and Drosophila cells shows that DDX3 is required for cell viability. Moreover, using RNAi, we show that DDX3 is required for expression of protein from reporter constructs. In contrast, we did not detect a role for DDX3 in nuclear steps in gene expression. Further insight into the function of DDX3 came from the observation that its major interaction partner is the multi-component translation initiation factor eIF3. We conclude that a primary function for DDX3 is in protein translation, via an interaction with eIF3.
Figures
References
-
- Linder P. Yeast RNA helicases of the DEAD-box family involved in translation initiation. Biol. Cell. 2003;95:157–167. - PubMed
-
- Rosner A, Rinkevich B. The DDX3 subfamily of the DEAD box helicases: divergent roles as unveiled by studying different organisms and in vitro assays. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007;14:2517–2525. - PubMed
-
- Hogbom M, Collins R, van den Berg S, Jenvert RM, Karlberg T, Kotenyova T, Flores A, Karlsson Hedestam GB, Schiavone LH. Crystal structure of conserved domains 1 and 2 of the human DEAD-box helicase DDX3X in complex with the mononucleotide AMP. J. Mol. Biol. 2007;372:150–159. - PubMed
-
- Chang PC, Chi CW, Chau GY, Li FY, Tsai YH, Wu JC, Wu Lee YH. DDX3, a DEAD box RNA helicase, is deregulated in hepatitis virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma and is involved in cell growth control. Oncogene. 2006;25:1991–2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

