Tissue-type plasminogen activator and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein induce Akt phosphorylation in the ischemic brain
- PMID: 18628488
- PMCID: PMC2556614
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-141630
Tissue-type plasminogen activator and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein induce Akt phosphorylation in the ischemic brain
Abstract
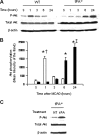
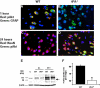
Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) is found in the intravascular space and in the central nervous system. The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) is expressed in neurons and in perivascular astrocytes. During cerebral ischemia, tPA induces the shedding of LRP's extracellular domain from perivascular astrocytes, and this is followed by the development of cerebral edema. Protein kinase B (Akt) is a serine/threonine kinase that plays a critical role not only in cell survival but also in the regulation of the permeability of the blood-brain barrier. We found that, in the early phases of the ischemic insult, the interaction between tPA and LRP induces Akt phosphorylation (pAkt) in perivascular astrocytes and inhibits pAkt in neurons. Coimmunoprecipitation studies indicate that pAkt and LRP's intracellular domain interact in perivascular astrocytes and that this interaction is dependent on the presence of tPA and results in the development of edema. Together, these results indicate that, in the early stages of cerebral ischemia, the interaction between tPA and LRP in perivascular astrocytes induces the activation of a cell signaling event mediated by pAkt that leads to increase in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier.
Figures


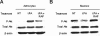
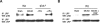
References
-
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1581–1587. - PubMed
-
- Wang YF, Tsirka SE, Strickland S, et al. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) increases neuronal damage after focal cerebral ischemia in wild-type and tPA-deficient mice. Nat Med. 1998;4:228–231. - PubMed
-
- Yepes M, Sandkvist M, Wong MK, et al. Neuroserpin reduces cerebral infarct volume and protects neurons from ischemia-induced apoptosis. Blood. 2000;96:569–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

