Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 14-substituted aromathecins as topoisomerase I inhibitors
- PMID: 18630891
- PMCID: PMC2538619
- DOI: 10.1021/jm800259e
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 14-substituted aromathecins as topoisomerase I inhibitors
Abstract
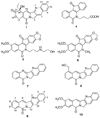
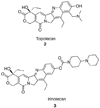
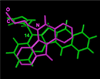
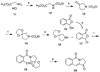
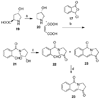
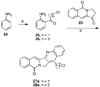
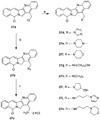
The aromathecin or "rosettacin" class of topoisomerase I (top1) inhibitors is effectively a "composite" of the natural products camptothecin and luotonin A and the synthetic indenoisoquinolines. The aromathecins have aroused considerable interest following the isolation and total synthesis of 22-hydroxyacuminatine, a rare cytotoxic natural product containing the 12 H-5,11a-diazadibenzo[ b, h]fluoren-11-one system. We have developed two novel syntheses of this system and prepared a series of 14-substituted aromathecins as novel antiproliferative topoisomerase I poisons. These inhibitors are proposed to act via an intercalation and "poisoning" mechanism identical to camptothecin and the indenoisoquinolines. Many of these compounds possess greater antiproliferative activity and anti-top1 activity than the parent unsubstituted compound (rosettacin) and previously synthesized aromathecins, as well as greater top1 inhibitory activity than 22-hydroxyacuminatine. In addition to potentially aiding solubility and localization to the DNA-enzyme complex, nitrogenous substituents located at the 14-position of the aromathecin system have been proposed to project into the major groove of the top1-DNA complex and hydrogen-bond to major-groove amino acids, thereby stabilizing the ternary complex.
Figures

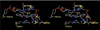
References
-
- Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: camptothecins and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:789–802. - PubMed
-
- Wang JC. Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: a molecular perspective. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;3:430–440. - PubMed
-
- Luzzio MJ, Besterman JM, Emerson DL, Evans MG, Lackey K, Leitner PL, McIntyre G, Morton B, Myers PL, Peel M, Sisco JM, Sternbach DD, Tong W, Truesdale A, Uehling DE, Vuong A, Yates J. Synthesis and antitumor activity of novel water soluble derivatives of camptothecin as specific inhibitors of topoisomerase I. J. Med. Chem. 1995;38:395–401. - PubMed
-
- Husain I, Mohler JL, Seigler HF, Besterman JM. Elevation of topoisomerase I messenger RNA, protein, and catalytic activity inhuman tumors: demonstration of tumor-type specficity and implications for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer. Res. 1994;54(2):539–546. - PubMed
-
- Thomas CJ, Rahier NJ, Hecht SM. Camptothecin: current perspectives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004;12:1585–1604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

