Persistent leatherback turtle migrations present opportunities for conservation
- PMID: 18630987
- PMCID: PMC2459209
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060171
Persistent leatherback turtle migrations present opportunities for conservation
Abstract
Effective transboundary conservation of highly migratory marine animals requires international management cooperation as well as clear scientific information about habitat use by these species. Populations of leatherback turtles (Dermochelys coriacea) in the eastern Pacific have declined by >90% during the past two decades, primarily due to unsustainable egg harvest and fisheries bycatch mortality. While research and conservation efforts on nesting beaches are ongoing, relatively little is known about this population of leatherbacks' oceanic habitat use and migration pathways. We present the largest multi-year (2004-2005, 2005-2006, and 2007) satellite tracking dataset (12,095 cumulative satellite tracking days) collected for leatherback turtles. Forty-six females were electronically tagged during three field seasons at Playa Grande, Costa Rica, the largest extant nesting colony in the eastern Pacific. After completing nesting, the turtles headed southward, traversing the dynamic equatorial currents with rapid, directed movements. In contrast to the highly varied dispersal patterns seen in many other sea turtle populations, leatherbacks from Playa Grande traveled within a persistent migration corridor from Costa Rica, past the equator, and into the South Pacific Gyre, a vast, low-energy, low-productivity region. We describe the predictable effects of ocean currents on a leatherback migration corridor and characterize long-distance movements by the turtles in the eastern South Pacific. These data from high seas habitats will also elucidate potential areas for mitigating fisheries bycatch interactions. These findings directly inform existing multinational conservation frameworks and provide immediate regions in the migration corridor where conservation can be implemented. We identify high seas locations for focusing future conservation efforts within the leatherback dispersal zone in the South Pacific Gyre.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
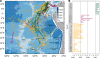

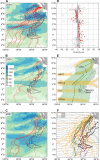
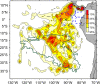
References
-
- Spotila JR, Reina RD, Steyermark AC, Plotkin PT, Paladino FV. Pacific leatherback turtles face extinction. Nature. 2000;405:529–530. - PubMed
-
- Martínez LS, Barragán AR, Muñoz DG, García N, Huerta P, et al. Conservation and biology of the leatherback turtle in the Mexican Pacific. Chelonian Conserv Biol. 2007;6:70–78.
-
- Santidrián-Tomillo P, Saba VS, Piedra R, Paladino FV, Spotila JR. Effects of illegal harvest of eggs on the population decline of leatherback turtles in Parque Nacional Marino Las Baulas, Costa Rica. Conserv Biol. 2008. In press. - PubMed
-
- Saba VS, Santidrián-Tomillo P, Reina RD, Spotila JR, Musick JA, et al. The effect of the El Niño Southern Oscillation on the reproductive frequency of eastern Pacific leatherback turtles. J Appl Ecol. 2007;44:395–404.
-
- Block BA, Costa DP, Boehlert GW, Kochevar RE. Revealing pelagic habitat use: the Tagging of Pacific Pelagics Program. Oceanologica Acta. 2003;25:255–266.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

