Transgenic overexpression of insulin receptor substrate 1 in hepatocytes enhances hepatocellular proliferation in young mice only
- PMID: 18631251
- PMCID: PMC2582588
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2008.00396.x
Transgenic overexpression of insulin receptor substrate 1 in hepatocytes enhances hepatocellular proliferation in young mice only
Abstract
Aim: The insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) is a multisite docking protein which plays a central role in the signal transduction of growth factors such as insulin and insulin-like growth factors (IGF-1 and IGF-2). It is found to be frequently overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
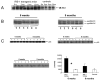
Methods: To study IRS-1 overexpression in hepatocytes in vivo, transgenic mice overexpressing IRS-1 exclusively in hepatocytes were created, showing enhanced hepatocyte proliferation in young animals. In the present study, the phenotype of IRS-1 transgenic animals was characterized over a period of two years. The livers of transgenic and control mice were analyzed for IRS-1 expression and phosphorylation, activation of the downstream mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade and phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase (PI3'K) and macroscopical and histological abnormalities.
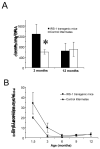
Results: The enhanced hepatocyte proliferation observed in young IRS-1 transgenic animals was no longer detectable in adult mice. Despite constitutive overexpression and phosphorylation of IRS-1, MAPK- and IRS-1-associated PI3'K activity were significantly reduced in older transgenic mice. Furthermore, no premalignant lesions or HCC were detected in IRS-1 transgenic animals up to the age of 24 months.
Conclusions: Therefore, additional mechanisms such as enhanced growth factor expression or impaired negative feedback control mechanisms may augment IRS-1 overexpression in human hepatocarcinogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of insulin receptor substrate-1 and hepatitis Bx genes causes premalignant alterations in the liver.Hepatology. 2009 Jun;49(6):1935-43. doi: 10.1002/hep.22856. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19475691 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol inhibits hepatocyte proliferation in insulin receptor substrate 1 transgenic mice.Gastroenterology. 1998 Dec;115(6):1558-65. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70036-8. Gastroenterology. 1998. PMID: 9834285
-
Stimulation of pancreatic beta-cell proliferation by growth hormone is glucose-dependent: signal transduction via janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) with no crosstalk to insulin receptor substrate-mediated mitogenic signalling.Biochem J. 1999 Dec 15;344 Pt 3(Pt 3):649-58. Biochem J. 1999. PMID: 10585851 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin receptor substrate 1 overexpression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells prevents transforming growth factor beta1-induced apoptosis.Cancer Res. 1996 Aug 1;56(15):3391-4. Cancer Res. 1996. PMID: 8758899
-
The mechanism of insulin-induced signal transduction mediated by the insulin receptor substrate family.Endocr J. 1999 Mar;46(Suppl):S25-34. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.46.suppl_s25. Endocr J. 1999. PMID: 12054114 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of insulin receptor substrate-1 and hepatitis Bx genes causes premalignant alterations in the liver.Hepatology. 2009 Jun;49(6):1935-43. doi: 10.1002/hep.22856. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19475691 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic value of microRNA-15b-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma and a bioinformatics investigation.Oncol Lett. 2019 Feb;17(2):1695-1713. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9748. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30675229 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of miR-15b-5p and toll-like receptor4 as potential novel diagnostic biomarkers for hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Dec 15;10:262-268. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.12.003. eCollection 2025 Feb. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39844891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Michalopoulos GK, DeFrances MC. Liver regeneration. Science. 1997;276(5309):60–6. - PubMed
-
- Rogler CE, Chisari FV. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 1992;12(3):265–78. - PubMed
-
- Pistoi S, Morello D. Liver regeneration 7. Prometheus’ myth revisited: transgenic mice as a powerful tool to study liver regeneration. Faseb J. 1996;10(8):819–28. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki Y, Zhang XF, Nishiyama M, Avruch J, Wands JR. Expression and phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 during rat liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(6):3805–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

