Reconstituting plant miRNA biogenesis
- PMID: 18632572
- PMCID: PMC2481364
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805207105
Reconstituting plant miRNA biogenesis
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
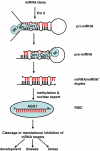
Figures
Comment on
-
The RNA-binding proteins HYL1 and SE promote accurate in vitro processing of pri-miRNA by DCL1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jul 22;105(29):9970-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803356105. Epub 2008 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18632569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carrington JC, Ambros V. Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science. 2003;301:336–338. - PubMed
-
- Mello CC, Conte D., Jr Revealing the world of RNA interference. Nature. 2004;431:338–342. - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe DC. RNA silencing in plants. Nature. 2004;431:356–363. - PubMed
-
- Chapman EJ, Carrington JC. Specialization and evolution of endogenous small RNA pathways. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:884–896. - PubMed
-
- Matranga C, Zamore PD. Small silencing RNAs. Curr Biol. 2007;17:R789–R793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

