Adiponectin blocks interleukin-18-mediated endothelial cell death via APPL1-dependent AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and IKK/NF-kappaB/PTEN suppression
- PMID: 18632660
- PMCID: PMC3259831
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M804236200
Adiponectin blocks interleukin-18-mediated endothelial cell death via APPL1-dependent AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and IKK/NF-kappaB/PTEN suppression
Abstract
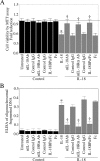
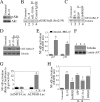
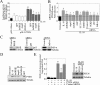
The adipocyte-derived cytokine adiponectin is known to exert anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects. In patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, circulating levels of adiponectin correlate inversely with those of the proinflammatory, proapoptotic cytokine interleukin (IL)-18. The opposing actions of IL-18 and adiponectin on both cell survival and inflammation led us to investigate whether adiponectin signaling antagonizes IL-18-mediated endothelial cell death and to identify the underlying molecular mechanisms. Treatment with IL-18 suppressed Akt phosphorylation and its associated kinase activity, induced IkappaB kinase (IKK)-NF-kappaB-dependent PTEN activation, and promoted endothelial cell death. Pretreatment with adiponectin stimulated APPL1-dependent AMPK activation, reversed Akt inhibition in a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent manner, blocked IKK-NF-kappaB-PTEN signaling, reduced caspase-3 activity, blocked Bax translocation, and inhibited endothelial cell death. The cytoprotective effect of adiponectin signaling was recapitulated by treatment with the pharmacological AMPK activator 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-riboside. Collectively, these results demonstrated that adiponectin reverses IL-18-mediated endothelial cell death through an AMPK-associated mechanism, which may thus have therapeutic potential for diminishing IL-18-dependent vascular injury and inflammation.
Figures
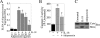
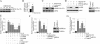

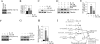
References
-
- Landmesser, U., Hornig, B., and Drexler, H. (2004) Circulation 109 Suppl. 1, II27—II33 - PubMed
-
- Kockx, M. M., De Meyer, G. R., Muhring, J., Jacob, W., Bult, H., and Herman, A. G. (1998) Circulation 97 2307-2315 - PubMed
-
- Dimmeler, S., Hermann, C., and Zeiher, A. M. (1998) Eur. Cytokine Netw. 9 697-698 - PubMed
-
- Diamant, M., and Tushuizen, M. E. (2006) Curr. Diab. Rep. 6 279-286 - PubMed
-
- Koenig, W., and Khuseyinova, N. (2007) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27 15-26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

