Features of 80S mammalian ribosome and its subunits
- PMID: 18632761
- PMCID: PMC2504317
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn424
Features of 80S mammalian ribosome and its subunits
Abstract
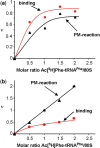
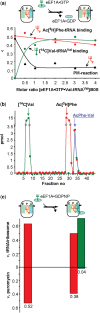
It is generally believed that basic features of ribosomal functions are universally valid, but a systematic test still stands out for higher eukaryotic 80S ribosomes. Here we report: (i) differences in tRNA and mRNA binding capabilities of eukaryotic and bacterial ribosomes and their subunits. Eukaryotic 40S subunits bind mRNA exclusively in the presence of cognate tRNA, whereas bacterial 30S do bind mRNA already in the absence of tRNA. 80S ribosomes bind mRNA efficiently in the absence of tRNA. In contrast, bacterial 70S interact with mRNA more productively in the presence rather than in the absence of tRNA. (ii) States of initiation (P(i)), pre-translocation (PRE) and post-translocation (POST) of the ribosome were checked and no significant functional differences to the prokaryotic counterpart were observed including the reciprocal linkage between A and E sites. (iii) Eukaryotic ribosomes bind tetracycline with an affinity 15 times lower than that of bacterial ribosomes (K(d) 30 microM and 1-2 microM, respectively). The drug does not effect enzymatic A-site occupation of 80S ribosomes in contrast to non-enzymatic tRNA binding to the A-site. Both observations explain the relative resistance of eukaryotic ribosomes to this antibiotic.
Figures
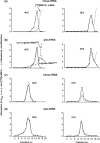
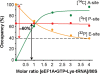
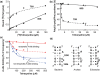
 were used to occupy the P site in 70S (dashed line) and 80S systems (solid line), respectively. The 100% corresponds to a ν value of 0.7 for both 70S and 80S ribosomes for non-enzymatic A-site binding and 0.83 and 0.6 for 70S and 80S ribosomes, respectively, for enzymatic A-site binding. (d) Parts of helices 34 from phylogenetic conservation maps superimposed onto the bacterial (E. coli), archaeal (Methanococcus jannaschii) and eukaryotic (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) 16S-type secondary structures (
were used to occupy the P site in 70S (dashed line) and 80S systems (solid line), respectively. The 100% corresponds to a ν value of 0.7 for both 70S and 80S ribosomes for non-enzymatic A-site binding and 0.83 and 0.6 for 70S and 80S ribosomes, respectively, for enzymatic A-site binding. (d) Parts of helices 34 from phylogenetic conservation maps superimposed onto the bacterial (E. coli), archaeal (Methanococcus jannaschii) and eukaryotic (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) 16S-type secondary structures (Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the eukaryotic ribosome.Science. 2010 Nov 26;330(6008):1203-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1194294. Science. 2010. PMID: 21109664
-
Leader sequences of eukaryotic mRNA can be simultaneously bound to initiating 80S ribosome and 40S ribosomal subunit.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012 Apr;77(4):342-5. doi: 10.1134/S0006297912040049. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012. PMID: 22809152
-
The assembly factor Reh1 is released from the ribosome during its initial round of translation.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 3;16(1):1278. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55844-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39900920 Free PMC article.
-
The function of the translating ribosome: allosteric three-site model of elongation.Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):1067-88. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90149-u. Biochimie. 1991. PMID: 1742351 Review.
-
Antibiotics and compounds affecting tanslation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Specific enhancement of aminoacyl-tRNA binding by methylaxnthines.Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;10(2):97-122. doi: 10.1007/BF01742203. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976. PMID: 768741 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of miRNAs, tRNAs and tRFs to Aberrant Signaling and Translation Deregulation in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 20;12(10):3056. doi: 10.3390/cancers12103056. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33092114 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the mammalian 80S initiation complex with initiation factor 5B on HCV-IRES RNA.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Aug;21(8):721-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2859. Epub 2014 Jul 27. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25064512
-
Perturbation of RNA Polymerase I transcription machinery by ablation of HEATR1 triggers the RPL5/RPL11-MDM2-p53 ribosome biogenesis stress checkpoint pathway in human cells.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(1):92-101. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1403685. Epub 2017 Dec 10. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 29143558 Free PMC article.
-
What Is the Impact of mRNA 5' TL Heterogeneity on Translational Start Site Selection and the Mammalian Cellular Phenotype?Front Genet. 2016 Aug 31;7:156. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00156. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27630668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A flexible loop in yeast ribosomal protein L11 coordinates P-site tRNA binding.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Dec;38(22):8377-89. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq711. Epub 2010 Aug 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20705654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Londei P. Evolution of translational initiation: new insights from the archaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005;29:185–200. - PubMed
-
- Pestova TV, Hellen CU. Functions of eukaryotic factors in initiation of translation. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2001;66:389–396. - PubMed
-
- Kisselev L. Polypeptide release factors in prokaryotes and eukaryotes: same function, different structure. Structure. 2002;10:8–9. - PubMed
-
- Qin Y, Polacek N, Vesper O, Staub E, Einfeldt E, Wilson DN, Nierhaus KH. The highly conserved LepA is a ribosomal elongation factor that back-translocates the ribosome. Cell. 2006;127:721–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

