General anesthetics have additive actions on three ligand gated ion channels
- PMID: 18633027
- PMCID: PMC2493416
- DOI: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31817b70c1
General anesthetics have additive actions on three ligand gated ion channels
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to determine whether pairs of compounds, including general anesthetics, could simultaneously modulate receptor function in a synergistic manner, thus demonstrating the existence of multiple intraprotein anesthetic binding sites.
Methods: Using standard electrophysiologic methods, we measured the effects of at least one combination of benzene, isoflurane (ISO), halothane (HAL), chloroform, flunitrazepam, zinc, and pentobarbital on at least one of the following ligand gated ion channels: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, glycine receptors and gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors.
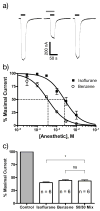
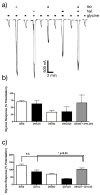
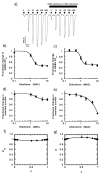
Results: All drug-drug-receptor combinations were found to exhibit additive, not synergistic modulation. ISO with benzene additively depressed N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors function. ISO with HAL additively enhanced glycine receptors function, as did ISO with zinc. ISO with HAL additively enhanced gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors function as did all of the following: HAL with chloroform, pentobarbital with ISO, and flunitrazepam with ISO.
Conclusion: The simultaneous allosteric modulation of ligand gated ion channels by general anesthetics is entirely additive. Where pairs of general anesthetic drugs interact synergistically to produce general anesthesia, they must do so on systems more complex than a single receptor.
Figures

Comment in
-
Does it add up?Anesth Analg. 2008 Aug;107(2):365-6. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31817e0e5b. Anesth Analg. 2008. PMID: 18633009 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hemmings HC, Jr, Akabas MH, Goldstein PA, et al. Emerging molecular mechanisms of general anesthetic action. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26:503–10. - PubMed
-
- Harris RA, Mihic SJ, Dildy-Mayfield JE, Machu TK. Actions of anesthetics on ligand-gated ion channels: role of receptor subunit composition. Faseb J. 1995;9:1454–62. - PubMed
-
- Ogata J, Shiraishi M, Namba T, et al. Effects of anesthetics on mutant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;318:434–43. - PubMed
-
- Miller PS, Da Silva HM, Smart TG. Molecular basis for zinc potentiation at strychnine-sensitive glycine receptors. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:37877–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

