G/T substitution in intron 1 of the UNC13B gene is associated with increased risk of nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 18633107
- PMCID: PMC2551697
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-0073
G/T substitution in intron 1 of the UNC13B gene is associated with increased risk of nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Genetic and environmental factors modulate the susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy, as initiating and/or progression factors. The objective of the European Rational Approach for the Genetics of Diabetic Complications (EURAGEDIC) study is to identify nephropathy susceptibility genes. We report molecular genetic studies for 127 candidate genes for nephropathy.
Research design and methods: Polymorphisms were identified through sequencing of promoter, exon, and flanking intron gene regions and a database search. A total of 344 nonredundant SNPs and nonsynonymous variants were tested for association with diabetic nephropathy (persistent albuminuria >/=300 mg/24 h) in a large type 1 diabetes case/control (1,176/1,323) study from three European populations.
Results: Only one SNP, rs2281999, located in the UNC13B gene, was significantly associated with nephropathy after correction for multiple testing. Analyses of 21 additional markers fully characterizing the haplotypic variability of the UNC13B gene showed consistent association of SNP rs13293564 (G/T) located in intron 1 of the gene with nephropathy in the three populations. The odds ratio (OR) for nephropathy associated with the TT genotype was 1.68 (95% CI 1.29-2.19) (P = 1.0 x 10(-4)). This association was replicated in an independent population of 412 case subjects and 614 control subjects (combined OR of 1.63 [95% CI 1.30-2.05], P = 2.3 x 10(-5)).
Conclusions: We identified a polymorphism in the UNC13B gene associated with nephropathy. UNC13B mediates apopotosis in glomerular cells in the presence of hyperglycemia, an event occurring early in the development of nephropathy. We propose that this polymorphism could be a marker for the initiation of nephropathy. However, further studies are needed to clarify the role of UNC13B in nephropathy.
Figures
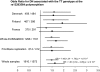
References
-
- Andersen AR, Christiansen JS, Andersen JK, Kreiner S, Deckert T: Diabetic nephropathy in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: an epidemiological study. Diabetologia 25:496–501, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Seaquist ER, Goetz FC, Rich S, Barbosa J: Familial clustering of diabetic kidney disease: evidence for genetic susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med 320:1161–1165, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Quinn M, Angelico MC, Warram JH, Krolewski AS: Familial factors determine the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with IDDM. Diabetologia 39:940–945, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Earle K, Walker J, Hill C, Viberti GC: Familial clustering of cardiovascular disease in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 326:673–677, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

