Four-jointed is a Golgi kinase that phosphorylates a subset of cadherin domains
- PMID: 18635802
- PMCID: PMC2562711
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1158159
Four-jointed is a Golgi kinase that phosphorylates a subset of cadherin domains
Abstract
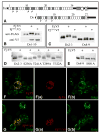
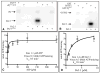
The atypical cadherin Fat acts as a receptor for a signaling pathway that regulates growth, gene expression, and planar cell polarity. Genetic studies in Drosophila identified the four-jointed gene as a regulator of Fat signaling. We show that four-jointed encodes a protein kinase that phosphorylates serine or threonine residues within extracellular cadherin domains of Fat and its transmembrane ligand, Dachsous. Four-jointed functions in the Golgi and is the first molecularly defined kinase that phosphorylates protein domains destined to be extracellular. An acidic sequence motif (Asp-Asn-Glu) within Four-jointed was essential for its kinase activity in vitro and for its biological activity in vivo. Our results indicate that Four-jointed regulates Fat signaling by phosphorylating cadherin domains of Fat and Dachsous as they transit through the Golgi.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

