Body mass and glucocorticoid response in asthma
- PMID: 18635892
- PMCID: PMC2556450
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200801-076OC
Body mass and glucocorticoid response in asthma
Abstract
Rationale: Obesity may alter glucocorticoid response in asthma.
Objectives: To evaluate the relationship between body mass index (BMI, kg/m(2)) and glucocorticoid response in subjects with and without asthma.
Methods: Nonsmoking adult subjects underwent characterization of lung function, BMI, and spirometric response to prednisone. Dexamethasone (DEX, 10(-6) M)-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and baseline tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha expression were evaluated by polymerase chain reaction in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and bronchoalveolar lavage cells. The relationship between BMI and expression of MKP-1 and TNF-alpha was analyzed.
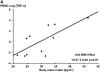
Measurements and main results: A total of 45 nonsmoking adults, 33 with asthma (mean [SD] FEV(1)% of 70.7 [9.8]%) and 12 without asthma were enrolled. DEX-induced PBMC MKP-1 expression was reduced in overweight/obese versus lean patients with asthma, with mean (+/- SEM) fold-induction of 3.11 (+/-0.46) versus 5.27 (+/-0.66), respectively (P = 0.01). In patients with asthma, regression analysis revealed a -0.16 (+/-0.08)-fold decrease in DEX-induced MKP-1 per unit BMI increase (P = 0.04). PBMC TNF-alpha expression increased as BMI increased in subjects with asthma, with a 0.27 unit increase in log (TNF-alpha [ng/ml]) per unit BMI increase (P = 0.01). The ratio of PBMC log (TNF-alpha):DEX-induced MKP-1 also increased as BMI increased in patients with asthma (+0.09 +/- 0.02; P = 0.004). In bronchoalveolar lavage cells, DEX-induced MKP-1 expression was also reduced in overweight/obese versus lean patients with asthma (1.36 +/- 0.09-fold vs. 1.76 +/- 0.15-fold induction; P = 0.05). Similar findings were not observed in control subjects without asthma.
Conclusions: Elevated BMI is associated with blunted in vitro response to dexamethasone in overweight and obese patients with asthma.
Figures


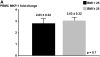
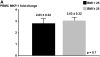





References
-
- Dolan CM, Fraher KE, Bleecker ER, Borish L, Chipps B, Hayden ML, Weiss S, Zheng B, Johnson C, Wenzel S. Design and baseline characteristics of the epidemiology and natural history of asthma: Outcomes and Treatment Regimens (TENOR) study: a large cohort of patients with severe or difficult-to-treat asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2004;92:32–39. - PubMed
-
- Weiss ST, Shore S. Obesity and asthma: directions for research. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;169:963–968. - PubMed
-
- Fantuzzi G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;115:911–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

