The helical structure of surfactant peptide KL4 when bound to POPC: POPG lipid vesicles
- PMID: 18636713
- PMCID: PMC2629594
- DOI: 10.1021/bi702551c
The helical structure of surfactant peptide KL4 when bound to POPC: POPG lipid vesicles
Abstract
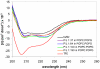
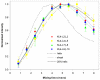
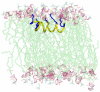
KL 4 is a 21-residue peptide employed as a functional mimic of lung surfactant protein B, which successfully lowers surface tension in the alveoli. A mechanistic understanding of how KL 4 affects lipid properties has proven elusive as the secondary structure of KL 4 in lipid preparations has not been determined at high resolution. The sequence of KL 4 is based on the C-terminus of SP-B, a naturally occurring helical protein that binds to lipid interfaces. The spacing of the lysine residues in KL 4 precludes the formation of a canonical amphipathic alpha-helix; qualitative measurements using Raman, CD, and FTIR spectroscopies have given conflicting results as to the secondary structure of the peptide as well as its orientation in the lipid environment. Here, we present a structural model of KL 4 bound to lipid bilayers based on solid state NMR data. Double-quantum correlation experiments employing (13)C-enriched peptides were used to quantitatively determine the backbone torsion angles in KL 4 at several positions. These measurements, coupled with CD experiments, verify the helical nature of KL 4 when bound to lipids, with (phi, psi) angles that differ substantially from common values for alpha-helices of (-60, -45). The average torsion angles found for KL 4 bound to POPC:POPG lipid vesicles are (-105, -30); this deviation from ideal alpha-helical structure allows KL 4 to form an amphipathic helix at the lipid interface.
Figures



References
-
- Goerke J. Pulmonary surfactant: functions and molecular composition. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Basis of Disease. 1998;1408:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Piknova B, Schram V, Hall SB. Pulmonary surfactant: phase behavior and function. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002;12:487–494. - PubMed
-
- Whitsett JA, Weaver TE. Mechanisms of disease: Hydrophobic surfactant proteins in lung function and disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;347:2141–2148. - PubMed
-
- Wright JR. Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2005;5:58–68. - PubMed
-
- Serrano AG, Perez-Gil J. Protein-lipid interactions and surface activity in the pulmonary surfactant system. Chem Phys Lipids. 2006;141:105–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

