Topical substance P increases inflammatory cell density in genetically diabetic murine wounds
- PMID: 18638272
- PMCID: PMC2497437
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2008.00400.x
Topical substance P increases inflammatory cell density in genetically diabetic murine wounds
Abstract
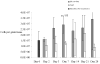
The neuropeptide substance P (SP) is a known inflammatory mediator released from cutaneous peripheral nerve terminals. SP effects on cellular composition in the cutaneous response to injury remain unclear. Based on our previous observations about SP effects on wound repair, we hypothesized that topical SP increases inflammatory cell density infiltration early after injury. A full-thickness 1.5 x 1.5 cm(2) wound was created on the dorsum of 8-9-week-old C57BL/6J-m+Lepr(db) mice (db/db). Wounds were treated daily with 300 muL of either normal saline (0.9% NaCl) or 10(-9) M SP for 7 days. Three wounds from each group were harvested at 2, 3, 7, 14, and 28 days. Samples underwent enzymatic digestion and were incubated with fluorescent-labeled antibodies. Using flow cytometry, cellular content and density for each sample was derived. Masson Trichrome stained histology specimens were prepared to confirm results. Cell density in the SP-treated wounds (11.3 x 10(7) cells/g tissue, standard deviation [SD]+/-1.5 x 10(7)) was greater than in NaCl-treated wounds (7 x 10(7) cells/g tissue, SD+/-2.3 x 10(7), p<0.05) at day 7 postwounding. SP significantly increased the density of leukocytes (2.1 x 10(7), SD +/-3.6 x 10(6) vs. 1.8 x 10(7), SD+/-4.9 x 10(5), p<0.02) 3 days after wounding and the density of macrophages (2.9 x 10(7), SD+/-7.5 x 10(6) vs. 1.3 x 10(7), SD+/-1.4 x 10(6), p<0.05) 7 days after wounding. There were no significant differences in endothelial cell, leukocyte, or macrophage density at later time points. Topical SP treatment increases early inflammatory density in the healing wounds of db/db mice. These data support a role for nerve-mediated inflammation in cutaneous wound repair.
Figures
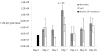
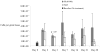
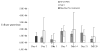
References
-
- Holzer P. Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience. 1988;24(3):739–68. - PubMed
-
- Dunnick CA, Gibran NS, Heimbach DM. Substance P has a role in neurogenic mediation of human burn wound healing. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1996;17(5):390–6. - PubMed
-
- Iwamoto I, Ueki IF, Borson DB, Nadel JA. Neutral endopeptidase modulates tachykinin-induced increase in vascular permeability in guinea pig skin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;88(3):288–93. - PubMed
-
- Holzer P. Neurogenic vasodilatation and plasma leakage in the skin. Gen Pharmacol. 1998;30(1):5–11. - PubMed
-
- Hughes S, Williams T, Brain S. Evidence that endogenous nitric oxide modulates oedema formation induced by substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;191:481–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

