Differential anti-atherosclerotic effects in the innominate artery and aortic sinus by the liver X receptor agonist T0901317
- PMID: 18639878
- PMCID: PMC2663528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.05.058
Differential anti-atherosclerotic effects in the innominate artery and aortic sinus by the liver X receptor agonist T0901317
Abstract
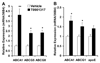
Activation of liver X receptors (LXRs) has been reported to reduce atherosclerosis in mouse models. However, this can be associated with enhanced liver de novo lipogenesis and elevation of plasma triglyceride-rich VLDL, which may limit its clinical use. In this study, we administered orally the LXR agonist T0901317 to male LDLR-/- mice fed a Western diet. This induced a persistent enhanced hypertriglyceridemia by largely increasing plasma triglyceride-rich VLDL. T0901317 treatment decreased atherosclerosis with a much more pronounced response and dose dependence in the innominate artery than in the aortic sinus. Lesions in the innominate artery were less complex containing mostly macrophage foam cells in T0901317-treated mice. However, in the aortic root, a significant reduction of atherosclerosis was seen only in the right coronary-related aortic sinus (RC) of T0901317-treated mice. Increasing the dose of T0901317 did not extend atheroprotection to the other sinuses of the aortic root. Lesions in the RC were less complex both in T0901317 and vehicle-treated mice with macrophage foam cells predominating. On the other hand, in T0901317-treated mice, the left coronary-related sinus (LC) lesions while not reduced in size, were more complex with a large fibrous cap and necrotic core, more collagen-positive areas, and variable macrophage foam cell content compared to vehicle-treated mice. These data suggest that activation of LXR by T0901317 had differential anti-atherosclerotic effects in two arterial regions in mice with hypertriglyceridemia.
Figures




References
-
- Cao G, Liang Y, Jiang XC, Eacho PI. Liver × receptors as potential therapeutic targets for multiple diseases. Drug News Perspect. 2004;17:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Repa JJ, Turley SD, Lobaccaro JA, Dietschy JM, Mangelsdorf DJ, et al. Regulation of absorption and ABC1-mediated efflux of cholesterol by RXR heterodimers. Science. 2000;289:1524–1529. - PubMed
-
- Wang N, Ranalletta M, Matsuura F, Peng F, Tall AR. LXR-induced redistribution of ABCG1 to plasma membrane in macrophages enhances cholesterol mass efflux to HDL. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1310–1316. - PubMed
-
- Yancey PG, Yu H, Linton MF, Fazio S. A Pathway-Dependent on ApoE, ApoAI, and ABCA1 Determines Formation of Buoyant High-Density Lipoprotein by Macrophage Foam Cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:1123–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

