Homeomorphic brain image segmentation with topological and statistical atlases
- PMID: 18640069
- PMCID: PMC2562468
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2008.06.008
Homeomorphic brain image segmentation with topological and statistical atlases
Abstract
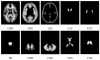
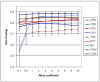
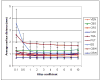
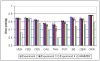
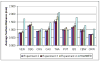
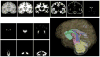
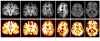
Atlas-based segmentation techniques are often employed to encode anatomical information for the delineation of multiple structures in magnetic resonance images of the brain. One of the primary challenges of these approaches is to efficiently model qualitative and quantitative anatomical knowledge without introducing a strong bias toward certain anatomical preferences when segmenting new images. This paper explores the use of topological information as a prior and proposes a segmentation framework based on both topological and statistical atlases of brain anatomy. Topology can be used to describe continuity of structures, as well as the relationships between structures, and is often a critical component in cortical surface reconstruction and deformation-based morphometry. Our method guarantees strict topological equivalence between the segmented image and the atlas, and relies only weakly on a statistical atlas of shape. Tissue classification and fast marching methods are used to provide a powerful and flexible framework to handle multiple image contrasts, high levels of noise, gain field inhomogeneities, and variable anatomies. The segmentation algorithm has been validated on simulated and real brain image data and made freely available to researchers. Our experiments demonstrate the accuracy and robustness of the method and the limited influence of the statistical atlas.
Figures



References
-
- Akselrod-Ballin A, Galun M, Gomori J, Brandt A, Basri R. Prior knowledge driven multiscale segmentation of brain mri. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI’07); Brisbane. october, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bazin P-L, Ellingsen L, Pham D. Digital homeomorphisms in deformable registration. Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging 2007 (IPMI’07); Kerkrade. july, 2007b. - PubMed
-
- Bazin P-L, Pham D. Statistical and topological atlas based brain image segmentation. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI’07); Brisbane. october, 2007a. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

