Insights into the regulation of 5-HT2A serotonin receptors by scaffolding proteins and kinases
- PMID: 18640136
- PMCID: PMC2629388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.06.048
Insights into the regulation of 5-HT2A serotonin receptors by scaffolding proteins and kinases
Abstract
5-HT(2A) serotonin receptors are essential molecular targets for the actions of LSD-like hallucinogens and atypical antipsychotic drugs. 5-HT(2A) serotonin receptors also mediate a variety of physiological processes in peripheral and central nervous systems including platelet aggregation, smooth muscle contraction, and the modulation of mood and perception. Scaffolding proteins have emerged as important regulators of 5-HT(2A) receptors and our recent studies suggest multiple scaffolds exist for 5-HT(2A) receptors including PSD95, arrestin, and caveolin. In addition, a novel interaction has emerged between p90 ribosomal S6 kinase and 5-HT(2A) receptors which attenuates receptor signaling. This article reviews our recent studies and emphasizes the role of scaffolding proteins and kinases in the regulation of 5-HT(2A) trafficking, targeting and signaling.
Figures
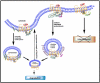
References
-
- Aghajanian GK. Electrophysiological studies on the actions of hallucinogenic drugs at 5-HT2 receptors in rat brain. NIDA Res Monogr. 1994;146:183–202. - PubMed
-
- Allen JA, Halverson-Tamboli RA, Rasenick MM. Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(2):128–140. - PubMed
-
- Backstrom JR, Price RD, Reasoner DT, Sanders-Bush E. Deletion of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor PDZ recognition motif prevents receptor phosphorylation and delays resensitization of receptor responses. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(31):23620–23626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

