Central actions of arginine vasopressin and a V1a receptor antagonist on maternal aggression, maternal behavior, and grooming in lactating rats
- PMID: 18640147
- PMCID: PMC2562530
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.06.013
Central actions of arginine vasopressin and a V1a receptor antagonist on maternal aggression, maternal behavior, and grooming in lactating rats
Abstract
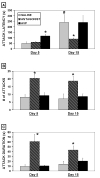
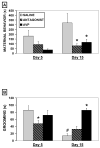
Maternal aggression is a robust type of aggression displayed by lactating female rats. Although arginine vasopressin (AVP) has been implicated in the control of male aggression, its involvement in maternal aggression has not been thoroughly investigated. Previous neuroanatomical studies suggest that AVP may mediate the display of aggression during lactation. In the current study, AVP and an AVP V1a receptor antagonist were centrally administered to primiparous rats on days 5 and 15 of lactation, and aggression, maternal behavior, and grooming were recorded. Although AVP did not affect the number of attacks or duration of aggression, it increased the latency to initiate aggression on day 5, in addition to decreasing maternal behavior and increasing grooming. Conversely, V1a antagonist treatment increased maternal aggression on both days of lactation, decreased maternal behavior on day 15, and decreased grooming on day 5. Thus, it appears that central AVP activity modulates maternal aggression, as well as maternal behavior and grooming behavior during lactation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vasopressin mediates enhanced offspring protection in multiparous rats.Neuropharmacology. 2010 Jan;58(1):102-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.06.032. Epub 2009 Jul 4. Neuropharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19580820 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of V1b receptors promotes maternal motivation to retrieve pups in the MPOA and impairs pup-directed behavior during maternal defense in the mpBNST of lactating rats.Horm Behav. 2016 Mar;79:18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.12.003. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Horm Behav. 2016. PMID: 26747375
-
Central V1b receptor antagonism in lactating rats: impairment of maternal care but not of maternal aggression.J Neuroendocrinol. 2014 Dec;26(12):918-26. doi: 10.1111/jne.12226. J Neuroendocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25283607
-
Maternal aggression in rodents: brain oxytocin and vasopressin mediate pup defence.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Oct 28;368(1631):20130085. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0085. Print 2013. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24167315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain vasopressin signaling modulates aspects of maternal behavior in lactating rats.Genes Brain Behav. 2019 Jan;18(1):e12517. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12517. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Genes Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 30221458 Review.
Cited by
-
Predator odor exposure of rat pups has opposite effects on play by juvenile males and females.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017 Jan;152:20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2016.08.008. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017. PMID: 27569603 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of early life social stress on maternal behavior and neuroendocrinology.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013 Feb;38(2):219-28. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.05.020. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013. PMID: 22770862 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally occurring variation in vasopressin immunoreactivity is associated with maternal behavior in female Peromyscus mice.Brain Behav Evol. 2012;80(4):244-53. doi: 10.1159/000341899. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Brain Behav Evol. 2012. PMID: 23018381 Free PMC article.
-
Normal maternal behavior, but increased pup mortality, in conditional oxytocin receptor knockout females.Behav Neurosci. 2010 Oct;124(5):677-85. doi: 10.1037/a0020799. Behav Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20939667 Free PMC article.
-
Early life social stress induced changes in depression and anxiety associated neural pathways which are correlated with impaired maternal care.Neuropeptides. 2015 Aug;52:103-11. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2015.05.002. Epub 2015 May 28. Neuropeptides. 2015. PMID: 26049556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banet M, Wieland U. The effect of intraseptally applied vasopressin on thermoregulation in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1985;14:113–116. - PubMed
-
- Beiderbeck DI, Neumann ID, Veenema AH. Differences in intermale aggression are accompanied by opposite vasopressin release patterns within the septum in rats bred for low and high anxiety. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2007;26:3597–3605. - PubMed
-
- Bester-Meredith JK, Martin PA, Marler CA. Manipulations of Vasopressin alter aggression differently across testing conditions in monogamous and non-monogamous Peromyscus mice. Aggressive Behavior. 2005;31:189–199.
-
- Blanchard RJ, Griebel G, Farrokhi C, Markham C, Yang M, Blanchard DC. AVP V1b selective antagonist SSR149415 blocks aggressive behaviors in hamsters. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 2005;80:189–194. - PubMed
-
- Bosch OJ, Kromer SA, Brunton PJ, Neumann ID. Release of Oxytocin in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus, but not central amygdala or lateral septum in lactating residents and virgin intruders during maternal defense. Neuroscience. 2004;124:439–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

