Second autologous stem cell transplantation for relapsed lymphoma after a prior autologous transplant
- PMID: 18640574
- PMCID: PMC3353768
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.05.021
Second autologous stem cell transplantation for relapsed lymphoma after a prior autologous transplant
Abstract
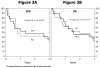
We determined treatment-related mortality, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) after a second autologous HCT (HCT2) for patients with lymphoma relapse after a prior HCT (HCT1). Outcomes for patients with either Hodgkin lymphoma (HL, n = 21) or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL, n = 19) receiving HCT2 reported to the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) were analyzed. The median age at HCT2 was 38 years (range: 16-61) and 22 (58%) patients had a Karnofsky performance score <90. HCT2 was performed >1 year after HCT1 in 82%. The probability of treatment-related mortality at day 100 was 11% (95% confidence interval [CI], 3%-22%). The 1-, 3-, and 5-year probabilities of PFS were 50% (95% CI, 34%-66%), 36% (95% CI, 21%-52%), and 30% (95% CI, 16%-46%), respectively. Corresponding probabilities of survival were 65% (95% CI, 50%-79%), 36% (95% CI, 22%-52%), and 30% (95% CI, 17%-46%), respectively. At a median follow-up of 72 months (range: 12-124 months) after HCT2, 29 patients (73%) have died, 18 (62%) secondary to relapsed lymphoma. The outcomes of patients with HL and NHL were similar. In summary, this series represents the largest reported group of patients with relapsed lymphomas undergoing SCT2 following failed SCT1, and with long-term follow-up. Our series suggests that SCT2 is feasible in patients relapsing after prior HCT1, with a lower treatment-related mortality than that reported for allogeneic transplant in this setting. HCT2 should be considered for patients with relapsed HL or NHL after HCT1 without alternative allogeneic stem cell transplant options.
Figures
References
-
- Vose JM, Rizzo DJ, Tao-Wu J, et al. Autologous transplantation for diffuse aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma in first relapse or second remission. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004;10:116–127. - PubMed
- Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1540–1545. - PubMed
-
- Khouri IF, Saliba RM, Giralt SA, et al. Nonablative allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation as adoptive immunotherapy for indolent lymphoma: low incidence of toxicity, acute graft-versus-host disease, and treatment-related mortality. Blood. 2001;98:3595–3599. - PubMed
-
- van Besien K, Thall P, Korbling M, et al. Allogeneic transplantation for recurrent or refractory non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with poor prognostic features after conditioning with thiotepa, busulfan, and cyclophosphamide: experience in 44 consecutive patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 1997;3:150–156. - PubMed
-
- Bishop MR, Hou JW, Wilson WH, et al. Establishment of early donor engraftment after reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to potentiate the graft-versus-lymphoma effect against refractory lymphomas. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003;9:162–169. - PubMed
-
- Faulkner RD, Craddock C, Byrne JL, et al. BEAM-alemtuzumab reduced-intensity allogeneic stem cell transplantation for lymphoproliferative diseases: GVHD, toxicity, and survival in 65 patients. Blood. 2004;103:428–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical